AIDS and HIV
amfAR’s Dr. Mathilde Krim dead at 91
AIDS pioneer’s life reflects LGBT/AIDS history
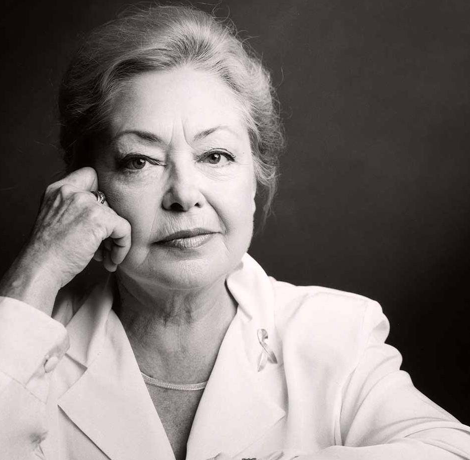
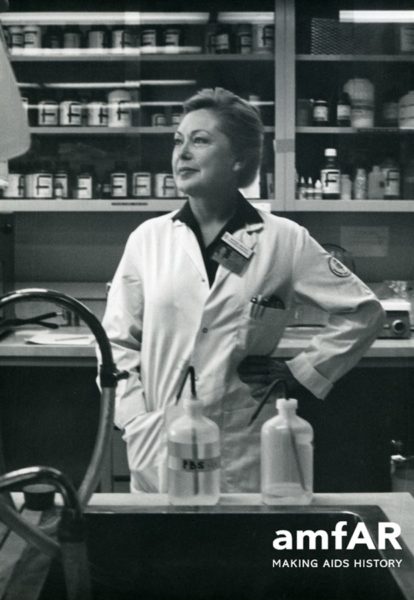
 Dr. Mathilde Krim, a wealthy, straight, scientific researcher who devoted her life to fighting HIV/AIDS, died on Monday (January 15, 2018) at her home in Kings Point, N.Y. at the age of 91.
Dr. Mathilde Krim, a wealthy, straight, scientific researcher who devoted her life to fighting HIV/AIDS, died on Monday (January 15, 2018) at her home in Kings Point, N.Y. at the age of 91.
“The board of trustees and staff of amfAR mourn the passing of our beloved Founding Chairman, Mathilde Krim, Ph.D. A pioneer in AIDS research and activism, Dr. Krim was at the forefront of scientific and philanthropic responses to HIV/AIDS long before the world fully understood its catastrophic global reach,” reads amfAR’s statement issued Tuesday morning.
“As amfAR’s founding chairman, and chairman of the board from 1990 to 2004, she was the heart and soul of the organization. She helped create it, supported it, kept it afloat more than once, and guided it with extraordinary dedication. She testified on Capitol Hill on several occasions, and was a driving force behind legislation that expanded access to lifesaving treatment and behind efforts to scale up federal funding for AIDS research. In August 2000, she was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom – the highest civilian honor in the United States,” the statement continued.
“Dr. Krim had such a profound impact on the lives of so many. While we all feel a penetrating sadness at the loss of someone we loved so deeply, it is important to remember how much she gave us and the millions for whom she dedicated her life. There is joy to be found in knowing that so many people alive today literally owe their lives to this great woman,” amfAR concluded.
New York-based Gay USA co-host and co-producer Andy Humm and longtime AIDS activist Peter Staley were the first to note Krim’s passing on their Facebook pages Monday night.
“My greatest AIDS hero died a few hours ago,” Staley wrote. “Dr. Mathilde Krim, founder of amfAR, warrior against homophobia and AIDS-related stigma, dedicated defender of science and public health, and mother-figure and mentor to countless activists, will leave a deep hole in the continued fight against AIDS — a fight she dedicated her life to. She was 91.”
“All honor to the great Dr. Mathilde Krim, founder of AmFAR (started as the AIDS Medical Foundation in 1983), who died today at 91–a giant in the fight against HIV and AIDS bringing both scientific and fundraising savvy and celebrities to the cause in the worst years of the AIDS pandemic. A tireless brilliant, calm, steady voice for healing, research, compassion and justice. Millions owe her their lives,” Humm wrote.
Krim’s passion to help people with AIDS was fueled by seeing newsreel footage as a teenager of the Nazi Holocaust during World War II. “What it did was to sensitize me against injustice. It’s really basically that—cruelty and injustice. And it’s a theme in my life,” Krim said in a 1990 interview.
”I volunteered for the [AIDS Medical Foundation] because I was incensed!” Krim said in a Nov. 1984 interview with the New York Times in her interferon laboratory at Sloan-Kettering Institute for Cancer Research, promoting the foundation’s first fundraiser—dinner and a fashion show headlined as Fashion Affair ’84. ”So many young men were dying, mostly intelligent and sophisticated young men, some of the city’s best products. And many would be dying abandoned or alone because they were afraid to contact their families.”
Krim’s life reads like a movie script with multiple odd juxtapositions—fashion, science, young gay men dying of AIDS while also being a “traditional wife” of a Hollywood studio head.
Krim was born Mathilde Galland in Cuomo, Italy in 1926. Her Swiss father was an agronomist and her mother, who was of Austrian descent, had grown up in Czechoslovakia. Her father moved the family to Geneva, Switzerland when she was 6.
As World War II started to break out in Europe, Krim heard stories about “sinister-sounding people called the Jews.”
At one point one summer, Krim worked as a gopher in the office of a lawyer who represented the United Jewish Appeal in Geneva. She saw the influx of Jewish refugees seeking asylum in Switzerland, only to be scoffed at and turned over to the Nazi-aligned Vichy French if they had no bank accounts.
“It made me sick. I was 16, 17, you know; one is impressionable. I was indignant. I decided, ‘Oh, no, I`m not going to live in a country that does this,’” she told an interviewer in 1990.
The epiphany came one day when she saw newsreel footage about the liberation of the Nazi concentration camps. “I went home and cried and told my parents. They said, ‘Oh, it may be exaggerated; it may not all be true.’ I kept crying; I was in a state of shock. And that lasted several days. To be young and to be unprepared for something like that-it was a terrible psychological shock,” Krim said. “I had never ever seen somebody die or dead, you know, and there I see human bones-most horrible pictures-being dumped from a truck into a hole in the ground, and this kind of thing.”
”I grew up not really knowing what was going on in the camps,” Krim said in 1988, ”though I knew that there was a good deal of anti-Semitism in Europe. My parents were no worse than the others, but they were like the others.”
But the “idea that people of my society were responsible for what had happened—it was very shocking to me. And I became very interested in knowing who were those Jews whom everybody had been after. Because I heard those terrible stories, that they were exploiting others, and I wanted to see for myself.”
In 1945, Krim went to the University of Geneva and met Jews from British-controlled Palestine. ”They were totally different from what I was told,” she said. ”I thought, ‘My God, if anything, I want to be like them.’ ”
Mathilde converted to Judaism and started working with a militant anti-British underground movement called the Irgun, run by a radical Zionist named Menachem Begin. Mathilde helped smuggle weapons to Begin from old French Resistance sympathizers. (When Begin became Israeli prime minister years later, he would be Krim’s houseguest.)
During this time, Krim studied biology in Geneva and, in 1953, received her Ph.D. She also fell in love with fellow Jewish radical David Danon and took his medical courses when he was away. The couple married and moved to Israel in early 1953. “We were in perfect harmony as long as the world was against us. But as soon as the pressure was off, we divorced,” she said
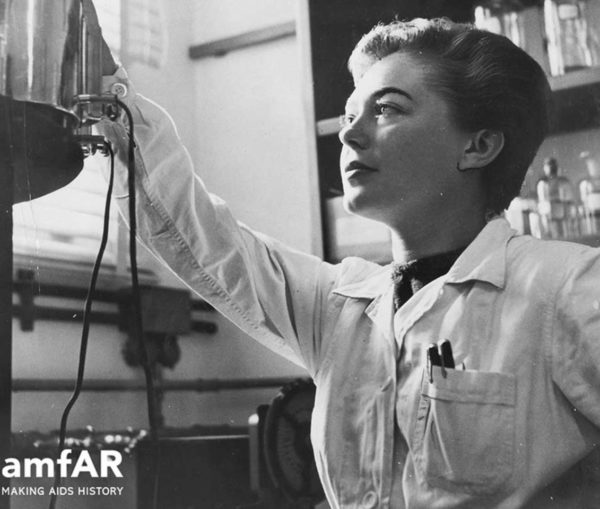

(Photo courtesy amfAR)
Krim became a junior researcher at the Weizmann Institute of Science and in 1956 was asked to give a tour to a honcho on the institute’s board of directors—New York movie executive Arthur Krim. They married in 1958 and moved to New York. Krim’s 7-year old daughter Daphna adjusted better than her mother. But eventually, Krim found a job at Cornell University Medical School where she studied virology, with the added benefit of being able to speak German, French, Italian, English, Hebrew and ”some Spanish.”

(Photo courtesy amfAR)
In 1962, Krim transferred to Sloan Kettering to pursue research into whether cancer might be caused by viruses. Her lawyer husband Arthur Krim, meanwhile, became chair of Orion Pictures and a prominent Democratic fundraiser and senior advisor to three Presidents—John F. Kennedy, Lyndon B. Johnson and Jimmy Carter. Mathilde Krim was the gracious hostess in their art-filled townhouse on East 69th Street when a president or presidential contenders such as Walter Mondale held court or stayed over.
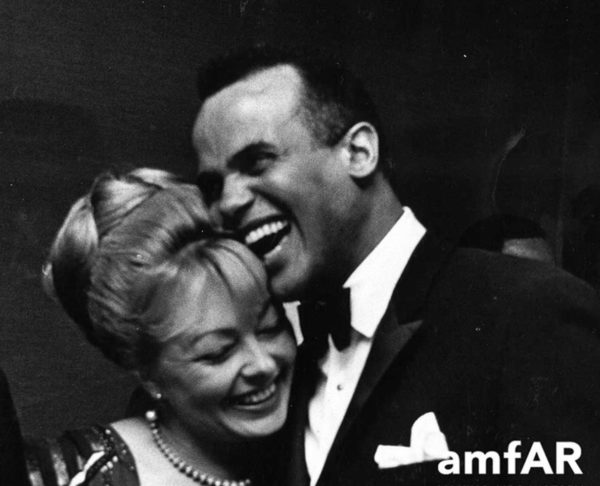

Krim with Harry Belafonte. (Photo courtesy amfAR)
Her husband was also a big fan of Democrat intellectual Adlai Stevenson, which spurred the couple’s interest in the civil rights movement in the US and Africa. With her passion to fight injustice, Krim became a member of the Congress on Racial Equality (CORE) and in 1966, joined the National Urban League. Meanwhile, from 1966 to 1968, Arthur Krim served as chair of the Democratic National Finance Committee.
By 1970, while writing a research report for a panel studying the history of cancer—a report that played a significant role in passage the National Cancer Act of 1971—Krim discovered an account of interferon, “a naturally occurring protein that seemed to ‘interfere’ with viruses, including those that caused tumors. Some experiments even indicated that interferon was effective against the tumors themselves,” according to the New York Times.
Krim was hooked on the possibility that interferon could lead to a more humane biological treatment for cancer, though other researchers were considerably less impressed, calling it ”imaginon,” accusing her of letting her heart rule her head. She was soon dubbed the Interferon Queen—a nicknamed she earned, using guile to get funding from the National Cancer Institute after being turned down. In 1975, she convinced the institute to sponsor an international conference on interferon and the night before she and her Hollywood-connected husband threw a party for 100 at their swank Manhattan townhouse.
”She more or less singlehandedly rescued the field from oblivion,” Martin S. Hirsch, an interferon expert at Massachusetts General Hospital, told the New York Times.
The institute gave her funding, as did the American Cancer Society, and by 1981, Krim had $6 million for her research, in addition to what she could raise from outside foundations and donors. Though touted as a possible cancer breakthrough, the research initially yielded mostly disappointments, treating only a rare form of leukemia. Her reputation as a detached scientist was questioned.

‘I probably could have done more if I had a husband less involved in things,” Krim told The New York Times in 1984. “Research is such a competitive life, and most of my colleagues are men who have wives who do everything at home. I know if I have to give a dinner for 100 people and be all dressed up and have my hair done, I can’t concentrate completely on my work.”
But in 1980, Krim’s attention was diverted by mysterious symptoms impacting patients of her research colleague, Dr. Joseph Sonnabend, who practiced medicine in Greenwich Village. Gay men were coming to him with enlarged lymph nodes, enlarged spleens and infections that failed to respond to treatment—and they had seriously compromised immune systems.
“Clearly, it was a biological infectious agent that was causing this disease and we also concluded that it must be sexually transmissible. My friend started using his medical practice as a source of clinical (blood) samples; he would send them around to experts to try to find another link, but nobody would figure out anything,” Krim later recalled. “In the spring of `81 Dr. Sonnabend came to tell us that some of his patients were dying, and our research activities were intensified.”

(Photo courtesy amfAR)
By then, Krim was the director of the interferon laboratory at Sloan-Kettering. “It was totally mind-blowing for a scientist who thinks she knows something to realize that, here in the middle of New York in the 20th century, a new disease could occur,” Krim said. “I personally didn’t believe for a minute that being gay could cause it. It was a scientific and medical puzzle that attracted my attention.”
Krim and Sonnabend worried that the mysterious disease was spreading but no one seemed to listen. The disease was killing those who “deserved it.”
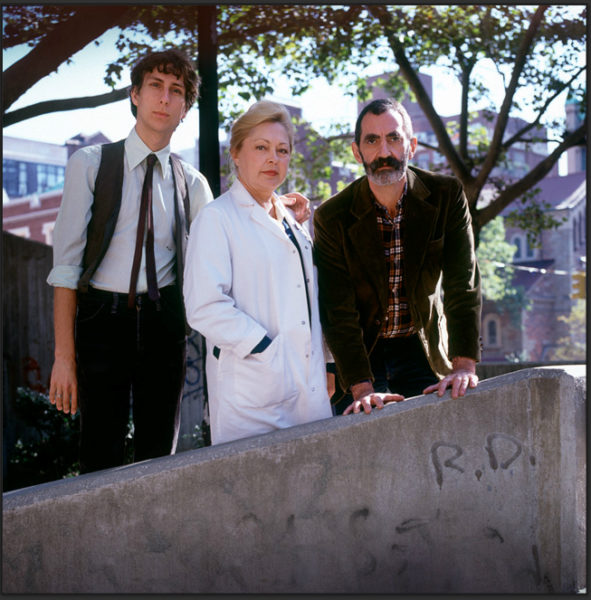

Michael Callen, Dr. Mathilde Krim, Dr. Joseph Sonnabend. (Photo Peter Serling courtesy Sean Strub)
Though her husband had gay friends, Krim told POZ Magazine, “I knew nothing about the gay community in 1981. Dr. Joseph Sonnabend sent me his patients, including Michael Callen, who told me what gay life was. That was quite an education! I was disgusted by the way society accused gay men of having created something terrible. When you think of it, the promiscuous life was caused by society—it didn’t allow gay men to get married or to have honest relationships. They had to hide.”
Krim’s compassion and hatred of injustice set in.
“In those early days, they were literally dying in the streets,” Krim told the Los Angeles Times in 2000. “[Gay men who had AIDS] lost their jobs, their apartments–their families turned away from them. It turned my stomach, it really impacted me and I decided this was something not to be tolerated.”
Unable to raise funding for their research, the colleagues decided to start their own organization in June 1983. The AIDS Medical Foundation (AMF) was co-founded by Krim—then 57 years old—Sonnabend, Nobel-prize winning scientist Dr. David Baltimore, singer, Sonnabend patient and AIDS activist Michael Callen (co-founder with fellow Sonnabend patient Richard Berkowitz of the People with AIDS Coalition), and respected philanthropist Mary Lasker.
The foundation was created to serve as a “scientific venture capitalist” to give provide seed money to researchers and scientists with promising AIDS-related projects that had been turned down for government grants. They wanted to be the AIDS version of the American Cancer Society. Arthur Krim kicked in the first $100,000 and within 90 days, Mathilde Krim had raised an additional $550,000. She also continued her interferon research, oversaw AMF operations, visited hospitals and clinics, and hosted fundraisers. Nothing was easy with efforts hampered by stigma. The AIDS Medical Foundation could not even list its full name in the lobby index in the Helmsley Building at 230 Park Avenue, having to list its office as A.M. Foundation.
Working together wasn’t easy, either. When Callen and Berkowitz wrote the first risk-reduction pamphlet under Sonnabend’s oversight entitled “How to Have Sex in an Epidenic: One Approach” espousing condom use, they approached Krim about publishing the safe sex guide through AMF. However, POZ founder Sean Strub writes in his book Body Counts, “Krim balked, fearing the frank language about anal sex was too risqué and would turn off potential donors. She did agree to let the foundation serve as a fiscal pass-through, so donations to print it would be tax-deductible.”
It was a serious concern, with donors from large corporations and Wall Street investment houses buying into the mythology of homosexuality.
”They felt that this was a disease that resulted from a sleazy life style, drugs or kinky sex—that certain people had learned their lesson and it served them right,” Krim told the New York Times in 1988.
”That was the attitude, even on the part of respectable foundations that are supposed to be concerned about human welfare.”
It sounded like the anti-Semitic propaganda she heard about Jews from the Nazis and Nazi sympathizers. ”I thought we had to enlarge our board and diversify—load it with straight people so that it’s not one more gay organization,” she said. To that end, she brought on board Elizabeth Kummerfeld, whose husband, Donald D. Kummerfeld, was president of Magazine Publishers of America. They set about planning for a $150-a-ticket November 1984 fashion show at the Tower Gallery, 45 West 18th Street, for which 50 designers, including Pauline Trigere, Bill Blass, Zandra Rhodes, Adolfo, Galanos and Calvin Klein, and other designers agreed to donate dresses and gowns. The show as narrated by Arlene Francis, followed by an auction and a buffet planned by Craig Claiborne. Former First Lady Rosalynn Carter, a friend of the Krims, attended.
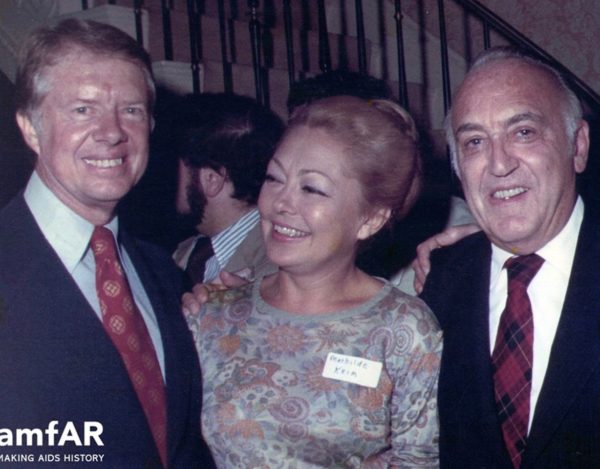

President Jimmy Carter and Mathilde Krim. (Photo courtesy amfAR)
Funding for Sonnabend’s research and perhaps a clinic was imperative. “We need such a clinic,” Krim told the New York Times in 1984, ”because it’s a place where patients can come without fear of discrimination. We deal with a population afraid of discriminatory practices, and that is not only gay men but drug users as well.”
The AIDS situation as ”very worrisome,” she continued. ”It’s not going to remain in the high- risk groups. All the evidence shows the disease is spreading in all directions, but people just aren’t worried anymore.”
At the same time, on the other side of the country in Los Angeles, pioneering AIDS researcher and immunologist Dr. Michael Gottlieb, was working with actress Elizabeth Taylor to create a foundation using $250,000 in start-up funding contributed by the late actor Rock Hudson, close friend of Taylor’s and a patient of Gottlieb’s. Krim called them about joining their efforts in the summer of 1985.
“Elizabeth Taylor and others were forming a like-minded organization on the West Coast, and I went out to visit her. She invited me to her house, and was immediately interested in working together, so we joined our organizations to form the American Foundation for AIDS Research,” Krim said in a 2015 interview. “From then on, Elizabeth dedicated herself to doing public speaking and even testifying in front of Congress.”
‘It was a shotgun marriage,” Gottlieb told Vanity Fair in 1992, a marriage of necessity between science and show business.

Dr. Mathilde Krim and Dame Elizabeth Taylor. (Photo courtesy amfAR)
“It did occur to me that having AmFAR on the East and West coasts might dilute it,” Taylor said. “Then I realized that Mathilde is a very powerful lady with a background that couldn’t have been more suitable. So it seemed like a very large and powerful decision.”
Mathilde Krim is “a smart woman and one of the most powerful I’ve ever met,” says Bill Misenhimer, who became amFAR’s first executive director, told the magazine. “You don’t fight her because she always wins. And AIDS is her life.”
“We complement each other very well,” Krim told VF, shrugging off questions about clashes. “I have a professional education in biology and medicine, and because I’m not a public figure I can work at the desk long hours. I mind the shop. Elizabeth contributes to projecting an image of the organization. She deals with the public very well.”
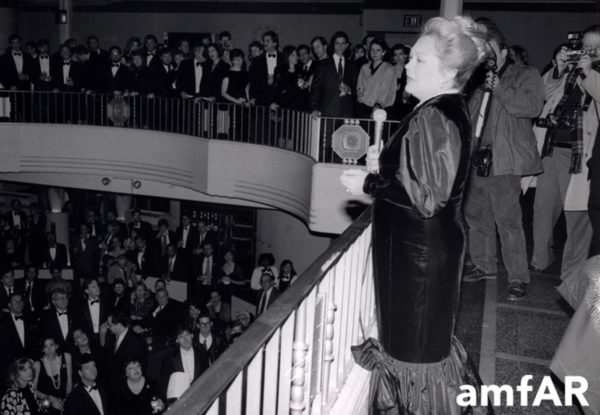
That was a quick lesson learned for the new national organization when Taylor appeared at the second amFAR fashion show in 1985 in Jacob K. Javits Convention Center in New York City. “We’d dutifully set in place security protection, but we didn’t make sufficient arrangements,” Krim recalled. “We didn’t realize she’d be mobbed by the crowd. She was atop a staircase with all the paparazzi and the public pushing behind—they almost threw her down.”
While Krim was gaining momentum with AMF, she was being unfavorably scrutinized at Sloan-Kettering by new president Paul A. Marks.
”I was told very clearly that I should tone down my visibility,” Krim told the NYT in 1988. ”He didn’t want his institute to become known as an AIDS hospital. Bad blood developed and at one point I decided, ‘This is enough.’”
(A spokesperson told the NYT that Sloan-Kettering continued to contribute to research on AIDS and interferon therapy.)
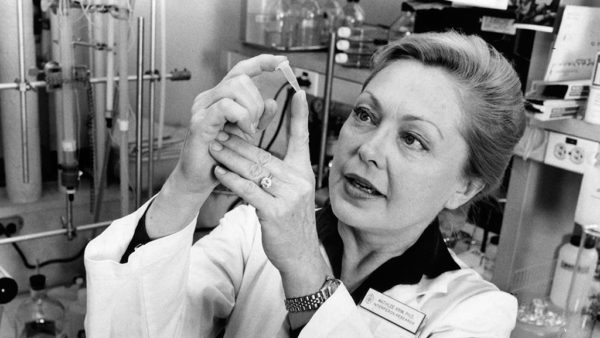
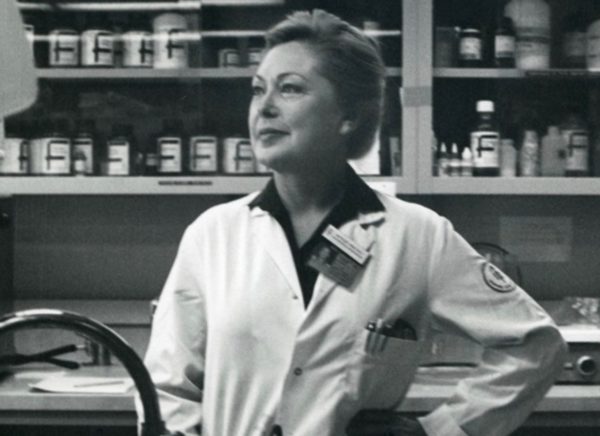
Krim at work in laboratory. (Photo courtesy amfar)
Krim left Sloan-Kettering in 1985 and subsequently became an associate research scientist at St. Luke’s-Roosevelt. But she was finished as a research scientist. In 2000, the Los Angeles Times noted that her besmirched, dogged research into interferon were vindicated: “Interferon has proved effective in inducing remissions in hairy-cell leukemia, and now is used to treat a long list of serious maladies: bladder cancer, renal cell cancer, hepatitis C, malignant melanoma, multiple myeloma, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and Kaposi’s sarcoma.”
Serving as AmFAR’s board chair suited her. ”I came to the conclusion that it’s better if I stay on the outside and help people inside the labs,” she said. ”I’m not such a genius that somebody else cannot do what I was doing. And these would be people who cannot do what I can.”
But Krim was able to use that scientific knowledge to challenge important issues that others took as fact. One of the most critical examples was in 1986—before ACT UP—when she took on the medical establishment over the testing of AZT. Per protocol, half the test subjects were given placebos, which Krim concluded would mean the placebo group could possible die by the time the effectiveness of the drug was determined. Though not a cure and saddled with harmful side effects, at least AZT could extend the dying person’s life for a few months.
”People who are on their last legs should get anything they want,” she said. ”We should just make sure we’re not killing them with it.”
Krim testfied before Congress that she opposed placebos in “double-blind” drug trials for people with full-blown AIDS. She lost out to two powerful opponents—National Cancer Institute top AIDS drug expert Samuel Broder and NIH AIDS research coordinator Anthony S. Fauci. But she eventually helped convince the NIH two years later to stop using placebos and to use AZT as the control instead. Additionally, Broder joined AmFAR’s scientific advisory committee, helping determine who gets grants.
One of amFAR’s biggest nights was the appearance of President Ronald Reagan, who had been invited by Taylor to speak at the benefit where Surgeon General Koop was among the honorees. It was Reagan’s second term in office and he had not yet addressed the AIDS epidemic. The benefit was the night before the third international conference on AIDS in Washington.
”He and his advisers must have thought that this was a good opportunity to appear in public in front of people who would behave reasonably well,” Krim told the New York Times in 1988.
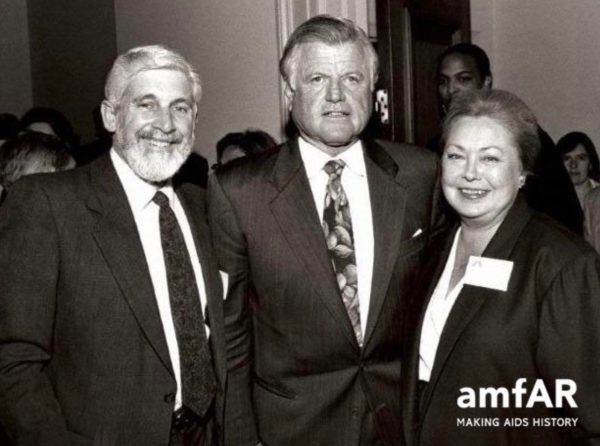

Krim with Senator Mervyn F. Silverman and Ted Kennedy. (Photo courtesy amfAR)
A Presidential speechwriter talked to AmFAR’s president Mervyn F. Silverman, who suggested that Reagan stress compassion and avoid the controversial systematic testing for the AIDS virus.
”The President said some of the right things, but he chose to mention testing,” Krim said. ”So that was the undoing of the rest of his speech. Even in our audience some people resented it, and he was in fact hissed, which was not the polite thing to do. But he should have known better.”
In fact, that May 31, 1987 speech contained harsh words reflective of his religious right domestic policy base. As of April 1987, the Centers for Disease Control reported 33,997 cases of AIDS in the US, with 19,658 deaths, no cure and the pall of stigma hanging over the country.
“If a person has reason to believe that he or she may be a carrier, that person has a moral duty to be tested for AIDS; human decency requires it. And the reason is very simple: Innocent people are being infected by this virus, and some of them are going to acquire AIDS and die,” Reagan said. “I’ve asked the Department of Health and Human Services to determine as soon as possible the extent to which the AIDS virus has penetrated our society and to predict its future dimensions.”
He said the AIDS immigration ban, testing for all federal prisoners, and possibly testing of veterans, “in addition to the testing already underway in our military and foreign service.”
“[Reagan’s speechwriters] didn’t know anything about AIDS, so we wrote the first half of the speech, where Reagan talked about compassion, justice, care — all the right things,” Krim told Vanity Fair. “We asked them to please not talk about mandatory testing, because it was not recommended scientifically, legally, or medically. We said it would elicit a furious reaction from the public. But one of Reagan’s advisers revised the speech and put it in.”
“The president mentioned mandatory testing and people jumped out of their seats. Then they started heckling him, so I jumped up and said, ‘Don’t be rude. This is your president and he is our guest,’” Taylor told the magazine.
Krim stuck with amFar until 2005 when she stepped down as founding chair, having helped build the organization into a prominent private supporter of AIDS research. Michael Musto wrote in POZ magazine, “As Dr. Mathilde Krim ‘a.k.a. the Mother of AIDS advocacy’ passes the amfAR torch to classy designer Kenneth Cole, her once-great institution may claim it’s not losing a legend but gaining a brand name. But can its new leader see past the bottom line to make amfAR not only fashionable but relevant again?”
amfAR would argue they are exceedingly relevant with their latest grants to three young scientists working on new HIV treatments and “leveraging vaccine research to help cure HIV.”
Krim does not leave this earth a saint—she disagreed with Taylor about going international, for instance, a debate Taylor won with the organization being renamed the Foundation for AIDS Research (amfAR, versus amFAR). To date amfAR has raised and invested an estimated $517 million for thousands of programs, according to the New York Times obituary on Krim.
And Taylor was not the only one with whom Krim disagreed, especially over political issues. In 1990, New York Mayor David N. Dinkins asked Krim about naming a city health commissioner. Krim recommended Indiana’s commissioner, Dr. Woodrow A. Myers Jr., who advocated names-reporting and possible quarantining of people with AIDS. Krim and others thought about it, stepped back, then re-endorsed Myers, then withdrew the endorsement. Myers was eventually appointed anyway and Krim was out in the cold.
“I think she’s exceptionally naïve politically,” playwright Larry Kramer told The Times. “We are all very angry with her, so far as one can ever get angry with Mathilde, because we love her so.”
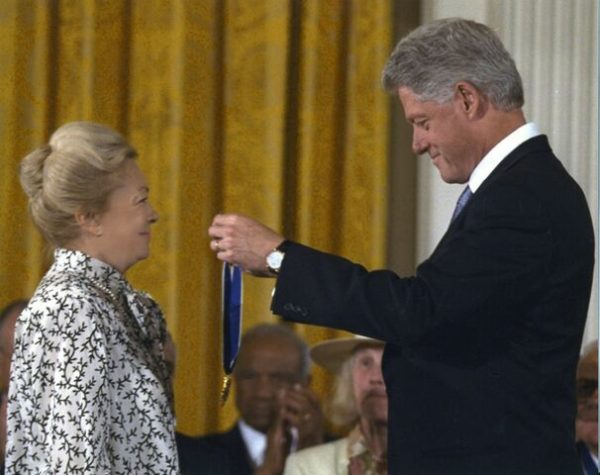

Krim receives honor from President Bill Clinton. (Photo courtesy amfAR)
But in 2000, Krim received the Presidential Medal of Freedom from President Clinton for her decades of AIDS-related work. And the National Portrait Gallery accepted two photographic portraits of Krim into its permanent collection in recognition of her leadership in the fight against HIV/AIDS—portraits by leading American photographers Annie Leibovitz and Joyce Tenneson.
”Everybody thinks of at least one person whom he has lost or is afraid for,” Krim told the New York Times in 1988. ”And I am no different. I have my little list.”
And now it’s Mathilde Krim who is on the list of AIDS heroes who have died.
“Dr. Krim was a close friend and mentor, and I am deeply saddened by this news. She dedicated her life to understanding the science behind the epidemic, and was a force to mobilize research around the globe that helped to save millions of lives and reduce the stigma attached to HIV/AIDS,” Elton John, Founder of the Elton John AIDS Foundation (EJAF). “The legacy of Dr. Krim’s deep commitment to ending HIV/AIDS will live on in the advocacy, action, and compassion of those that follow her lead. We would not be where we are today without her, and we must continue to work tirelessly to further understand and prevent the disease. My thoughts are with her family at this time, she was a true hero.”

“For over three decades, I have witnessed one of the most remarkable women in my lifetime fight against the plague of HIV/AIDS,” longtime LGBT rights activist/author David Mixner, who was honored by amfAR. “Dr. Krim was there when no one else would even touch us. There was not one day in the fight against this epidemic that she wasn’t working by our side. Dr. Mathilde Krim was a true legend, heroine and a dear friend.”
“We have lost an inspirational, tireless, and catalytic leader of our movement,” said Mark Harrington, Treatment Action Group’s Executive Director. “Dr. Krim understood the gravity of the epidemic, in its earliest and darkest days, and was driven by her own remarkable intelligence, fierce commitment to civil rights and social justice, extraordinary social and political networks, and true grit to galvanize funders, scientists, policy leaders, and activists toward a single cause: ending HIV and AIDS as a threat to humanity.”
“I genuinely believe that we wouldn’t be where we are today without Dr. Krim’s brilliance, determination, and mobilization,” said Tim Horn, Deputy Executive Director of HIV & HCV Programs at TAG. “Beyond her unparalleled contributions to HIV/AIDS research fundraising and awareness, she was an interminable source of strength, support, and wisdom for countless activists over the years.”
“TAG has lost a matriarch of our family, a leader in our movement, and a steadfast supporter of our work,” said Barbara Hughes, President of TAG’s Board of Directors. “We mourn Dr. Krim’s passing and join amfAR and so many leaders in the fight against HIV/AIDS in remembering her work and life.”

TAG: Photo (bottom center): By Rob Klein, 2010. From left, Alby Maccarone (Director Emeritus), Dr. Mathilde Krim, Mark Harrington (Executive Director), and Barbara Hughes (President) at the 2010 TAG Research in Action Awards.
“Matilda Krim was a pioneering legend. Her compassion and foresight at the very beginning of the epidemic played a crucial role in mobilizing support to fight the battle against AIDS,” says Michael Weinstein, president of AIDS Healthcare Foundation.
“Even though Mathilde has been gone for a while from any active Public role, it does feel like the end of an era,” says Sean Strub, founder of POZ Magazine and out HIV-positive mayor of Milford, Pennsylvania.
“Mathilde used her resources, curiosity, tenacity and heart to provide leadership and build support to fund AIDS research at a time when few of her peers were willing to do so. The history of the epidemic is intertwined with her own; she was persistent, unflappable and prescient.”
“I became aware of Mathilde Krim around 1988, while I was working as the staff writer for the National AIDS Network, a coalition of community-based AIDS service organizations in Washington, D.C. By then Dr. Krim was already legendary in the HIV-AIDS community,” says John-Manuel Andriote, author of Victory Deferred: How AIDS Changed Gay Life in America. “It’s hard to overstate the importance of Dr. Krim and Elizabeth Taylor’s “mainstream” (and heterosexual) cachet in helping to ratchet down the fear and stigma associated with what then was a deadly new illness perceived as mainly afflicting gay men.”
“As an HIV positive man who has been living with the virus for over 13 years, I know that I would not be alive today without the efforts of Dr. Mathilde Krim,” says out New York City Council Speaker Corey Johnson. “I met her during my first trip to New York City, at age 18. Little did I know the important role she would play in my life. My thoughts and prayers go to the family and friends of Dr. Krim. Her legacy will live on in the countless lives she saved.”
AMFAR VIDEO:
AIDS and HIV
From ACT UP to apps: A candid conversation with MISTR founder Tristan Schukraft
As HIV prevention ushers in a new era, Schukraft reflects on the evolution of sexual healthcare and the power of stigma-free prevention

It was not too long ago that an HIV diagnosis was read as a death sentence. In its earlier decades, the HIV/AIDS crisis was synonymous with fear and loss, steeped in stigma. Over recent years, open conversation and science have come together to combat this stigma while proactively paving the way for life-saving treatments and preventive measures like PrEP. Now, in 2026, with discreet and modern platforms that meet people where they’re at in their lives, HIV prevention has evolved from hushed words of warning into something far more sex-positive and accessible. Game-changing services like MISTR are a testament to this shift, showing our community that healthcare doesn’t have to feel clinical or shaming to work. It can be empowering and, dare I say, celebratory.
Few people embody this evolution quite like Tristan Schukraft, founder of MISTR. With one hand in healthcare and the other high-fiving through queer nightlife, Schukraft gets that, from the bar to the bedroom and beyond, prevention happens in person and in real life. His approach has helped turn PrEP, DoxyPEP, and testing into normalized parts of our daily queer life, reaching hundreds of thousands of people across the US.
In our conversation, Schukraft shares candidly about stigma, policy, and why the future of sexual health depends on keeping it real.
You have one hand in healthcare and the other in nightlife and queer spaces. Can you share with us how these two spheres impact and inform each other? How do they impact and inform you?
Honestly, for me, they’ve never been separate. Nightlife and queer spaces are where people meet, date, hook up, fall in love, and make friends. That’s real life. Being in queer spaces all the time keeps me grounded and reminds me who we’re building MISTR for.
MISTR markets sexual health in a sex-positive, stigma-free fashion. Can you share with us how you measure the impact of this approach?
This year, we held the first-ever National PrEP Day. Dua Lipa performed, and Cardi B was there. After the event, Cardi B went on her Instagram live to encourage people to sign up for PrEP.
When you make sexual health stigma-free and sex positive, people talk about it. We see it in how people use the platform. When 700,000 people are willing to sign up, get tested, start PrEP, and add things like DoxyPEP, that tells us we’ve made it feel safe and normal instead of scary or awkward. And then we see it in the results. Since we expanded DoxyPEP, STI positivity among our patients dropped by half.
How have you seen the conversation of sexual health in our LGBTQ+ community change in mainstream culture in recent years?
Ten years ago, nobody was casually talking about PrEP, and if they did, it likely referenced one being a Truvada whore. Now it’s part of the culture. Popstars like Troye Sivan post pictures of their daily PrEP pill on social media. Cardi B goes on Instagram Live telling people to get on PrEP.
For many sexually active gay men, taking PrEP is simply part of the gay experience. For people in more remote areas, it might not be as talked about. Particularly in rural or more conservative places, MISTR can be a life-changing option. No awkward visits to the family doctor or the local pharmacy where everybody knows your business. It’s all done discreetly online and shipped straight to your door.
You have publicly argued that cuts to government HIV prevention funding are of high risk. Would you please elaborate for us on what those budget decisions mean on an individual level?
It means real people fall through the cracks. Someone doesn’t get tested. Someone waits too long to start PrEP. Someone finds out they’re HIV-positive later than they should have. Community clinics will be the hardest hit, especially those in underserved communities. The good news is that MISTR is ready to help people who might lose their access to care. All you need to do is sign up at mistr.com, and it’s totally free with or without insurance.
From your (and MISTR’s) perspective, how do these funding cuts threaten ongoing efforts to end the HIV epidemic?
For the first time, we have all the tools to end HIV. If everybody who is HIV negative is taking PrEP and everyone HIV+ is virally suppressed, we can end all new HIV transmissions in the United States. We have everything we need today. All we need is to get more people on PrEP. Cutting funding risks losing that momentum. Ending HIV requires scale and consistency. Every time funding gets cut, you lose momentum, trust, and infrastructure, and rebuilding that takes years.
HIV transmissions don’t pause because budgets change.
In our current climate of decreased federal investment, what role do you feel private healthcare and business should play in sexual health?
With reports that the current administration is considering cuts to HIV and prevention funding, we face a moment of reckoning. At the same time, some employers are seeking to exclude PrEP and HIV prevention from their coverage on religious freedom grounds. If these challenges succeed, and if federal funding is slashed, the consequences for public health will be devastating. But this is where the private sector must step up to fill the gap, bridge divides, and deliver results.
Businesses have the power and platform to normalize HIV prevention and drive measurable outcomes. At MISTR, we see firsthand what’s possible: since introducing DoxyPEP, STI positivity rates among our patients have been cut in half. But it’s not just about medication. It’s about messaging.
Our sex-positive, stigma-free marketing speaks directly to our community, making sexual health part of everyday life. No awkward doctor visits, no needles, no paperwork — just free online PrEP and STI testing, prescribed by real physicians and delivered to your door. That kind of impact could grow exponentially if more employers embraced this approach and made HIV prevention part of their employee wellness programs.
Employers, this is your call to action. Start by making sure your health plans cover PrEP and DoxyPEP. Partner with platforms like MISTR to give employees private, stigma-free access to care. Offer on-site testing. Talk openly about sexual health, not just during Pride, but every day of the year. This is not political — this is about protecting lives, strengthening communities, and building a healthier, more productive workforce. Because healthy employees aren’t just good for public health — they’re good for business.
When the private sector steps up, outcomes improve. And when businesses align with platforms like MISTR, scaling impact isn’t just possible — it’s happening.
Has MISTR experienced any direct effects from these recent shifts in public health funding?
MISTR’s unique model is totally free for patients with or without insurance, and we don’t cost the government or taxpayers a penny. We are scaling up our efforts to reach people who might be losing their access or care.
What would be your message to policymakers who are considering further cuts to HIV/AIDS programs?
During his first term, President Donald Trump committed unprecedented resources to the Ending the HIV Epidemic initiative here at home. Bipartisan support has shown what’s possible when bold leadership meets smart strategy. To policymakers: I urge you to reconsider any cuts to HIV prevention funding. This is not the time to pull back. It’s the time to push forward. Ending HIV is within reach — but only if government, private industry, and community organizations stand together.
What is one perhaps overlooked win from last year that impacted you on a personal level?
Seeing our STI positivity rate drop by half after expanding DoxyPEP.
Looking at the year ahead, what are MISTR’s most significant priorities for sexual health in 2026?
Expanding access, especially in the South and in communities that still get left out. Rolling out injectable PrEP. And just continuing to make sexual healthcare easier and more normal.
Is MISTR planning to integrate injectable PrEP into the mix?
Yes, absolutely. Long-acting PrEP is a game-changer, especially for people who struggle with daily pills. We’re rolling it out through a hybrid model: telehealth plus in-person injections in key LGBTQ+ neighborhoods.
As you just mentioned, MISTR reported cutting STI positivity rates in half through expanded DoxyPEP access last year (mad props). What do you think allowed you to accomplish this?
We made it easy, normalized it, and bundled it into care. No stigma, no hoops, no lectures. When you remove friction, people take care of themselves.
If you could eliminate from our collective consciousness one particular myth or stigma about sexual health, what would it be?
Sexual health should be talked about in the open, and we can have fun with it! I threw a party in October for National PrEP Day. How many parties have you been to celebrating sexual health? You should go to more.
What were the most significant obstacles or setbacks you saw some of your patients face in accessing PrEP and STI prevention services in the recent past?
Stigma, paperwork, insurance, provider judgment, and just navigating a system that was never designed for them.
Looking at the next chapter, what would you like to see MISTR accomplish next? And I have to ask, what’s next for you?
For MISTR: scale, injectables, and getting more HIV+ utilizing MISTR long-term HIV care. I started MISTR with the goal of ending HIV, so this year, next year, and as long as it takes, I want to make history and end HIV.
For me: staying close to the community, building things that matter, and making sure we never lose sight of the humans behind the metrics.
For more information, head to HeyMistr.com.
This article is part of LA Blade’s January health series.
AIDS and HIV
Community is the cure: AIDS Walk LA returns to fight HIV and funding cuts
AIDS Walk Los Angeles returns to West Hollywood on October 12 with the theme ‘Community Is the Cure,’ highlighting the vital role of unity, radical community action, and advocacy in the fight against HIV/AIDS, stigma, and government funding cuts

APLA Health, a nonprofit providing HIV care, prevention, and sexual health services, announced the return of AIDS Walk Los Angeles on Sunday, October 12, 2025, starting from West Hollywood Park. This year’s theme, “Community Is the Cure,” emphasizes the role of unity in advancing progress against HIV/AIDS and supporting those affected.
Walk day will feature a live performance from RuPaul’s Drag Race star Heidi N Closet, DJ sets, and community booths. Following the celebration, walkers will make their way through the streets of West Hollywood.
“This event was born out of urgency, and it’s just as relevant today,” said Craig E. Thompson, CEO of APLA Health. “We’ve made incredible progress in the fight against HIV, but that progress is under direct threat from funding cuts and political attacks. Now is the time to show that we won’t be silenced or set back.”
Since its inception forty years ago, AIDS Walk Los Angeles has grown into one of the largest HIV/AIDS fundraising events in the world, raising nearly $100 million. Proceeds fund APLA Health’s services, including HIV specialty care, sexual health services, food and nutrition support, and housing assistance.
“The HIV/AIDS epidemic has always shown us that progress happens when people come together, when patients, neighbors, families, activists, and health providers stand shoulder to shoulder. Today, with funding under attack and stigma resurfacing, unity is not optional. ‘Community Is the Cure’ is a reminder that science alone isn’t enough. We need collective willpower, advocacy, and solidarity to ensure everyone has access to the care and dignity they deserve,” Thompson said.
Cuts to Medicaid, the Ryan White Program, and prevention funding threaten access to medications, housing assistance, and food security. “Here in Los Angeles, where tens of thousands rely on these programs, even modest reductions can push people back into crisis. AIDS Walk Los Angeles helps fill some of those gaps, but philanthropy cannot fully replace the government’s responsibility,” Thompson explained.
Communities of color, the medically underserved, people living in poverty, and those experiencing homelessness are disproportionately affected. “The barriers aren’t medical. They’re structural: stigma, lack of insurance, unstable housing, and underfunded safety-net services. The administration is underinvesting in the very programs designed to break down these barriers. Until that changes, inequities in HIV prevention and care will persist,” he said.
Funds raised by the walk provide housing, groceries, case management, and access to medical care. Thompson shared the story of one patient who had lost housing and had to choose between medication and meals. “Through AIDS Walk–funded programs, we were able to connect him to stable housing, consistent medical care, and our food pantry. Today, he is virally suppressed, working again, and mentoring others who are newly diagnosed with HIV. Stories like his are common, and they remind us that cuts aren’t just numbers on a spreadsheet, they’re setbacks in real people’s lives.”
Beyond fundraising, AIDS Walk LA is a platform for advocacy. “When thousands of people flood the streets of West Hollywood, it’s a visible reminder to our community that HIV/AIDS has not gone away and to policymakers that their decisions have life-or-death consequences. The walk puts pressure on elected officials to fund programs, fight stigma, and stand up for people affected by HIV,” Thompson said.
He urged the public to take action beyond walking and donating. “Call your elected officials. Demand that HIV services remain fully funded. Show up for community hearings. Support housing initiatives. Share facts on social media to counter stigma. And, importantly, talk. Without continued conversation about HIV/AIDS and sexual health, we jeopardize the incredible advancements we’ve made in HIV care and prevention.”
Thompson also framed the walk as part of a broader activist approach. “Radical action today means showing up for one another in tangible ways, housing someone, feeding someone, advocating for someone, and refusing to accept policies that erase people’s humanity. As our theme emphasizes, when politicians fail us, COMMUNITY IS THE CURE. For participants in AIDS Walk LA, it means recognizing that the walk is just the beginning. Each person can be a messenger, an advocate, and an ally in daily life. When we work together to get people connected to support services, the collective action is radical because it insists on care and dignity in a time when those values are under attack.”
“Activism ensures policymakers cannot quietly dismantle programs. Community solidarity means that no one gets left behind. Public pressure creates accountability. When thousands unite at AIDS Walk LA, it demonstrates the broad mandate to keep fighting until HIV is no longer a public health crisis. That unity is as important as any medical breakthrough,” Thompson concluded.
For more information on AIDS Walk Los Angeles and how to register, visit https://AIDSWALK.LA.
AIDS and HIV
“If not now, when?” Journalist and activist Karl Schmid is reshaping how we talk about HIV/AIDS
The Blade sits down with the award-winning host to talk about stigma and his latest initiative – taking HIV education onto the runway
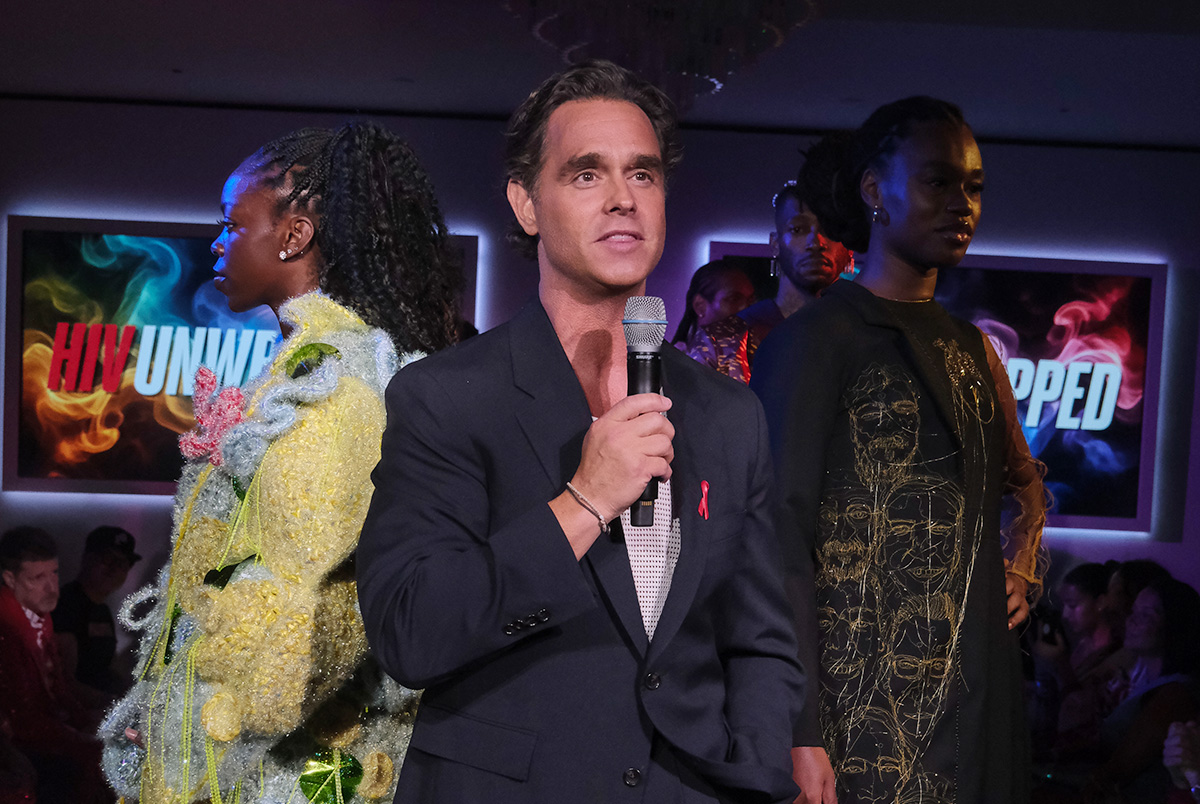

Karl Schmid has long been a staple in queer news and media. Hailing from Australia, Schmid grew accustomed to the limelight from a young age, and eventually made a successful transition into American network television through his work on red carpets for ABC.
In 2018, he would be thrust into the spotlight for a different reason. Despite repeated warnings from professional acquaintances, Schmid came out as HIV positive to share his story, wear down stigmas, and to educate people about important and misunderstood science like the concept of undetectable equals untransmittable.
And so, Schmid would grow accustomed to renewal. In 2019, he launched Plus Life Media, a platform that shares HIV resources, education, and stories of resilience from people living with HIV/AIDS. He was part of the team behind the Emmy-nominated short documentary, Marty’s Place: Where Hope Lives: an intimate look into a housing cooperative created in the 1990s to support people with HIV/AIDS. Late last week, he flew to New York for the U.S. debut of his latest initiative: HIV Unwrapped. The project pairs researchers and scientists in HIV studies with fashion design students, culminating in a runway show that features bold reimaginings and interpretations of crucial science.
The Blade spoke with Karl about the cross-pollination in his own life and career, and how his latest effort is shaping the way he blends activism and media to reinvigorate conversations around HIV/AIDS.
HIV Unwrapped feels like a really interesting pivot into a different kind of modality and platform for you. Can you tell me more about the initiative and how it fits into your legacy of activism and work?
Well, HIV Unwrapped came out of Australia and this wonderful activist named Brent Allan, who I’m good friends with. And Brent had been at, I think, the WorldPride, or something that was happening in Australia, and there was an exhibition where they paired some engineers and science people of varying professions with a fashion designer to try and illustrate their work.
And he thought, “Wow, what a great way to maybe try and interpret HIV science and reignite the conversation around HIV.” So it started in Melbourne, Australia, and it was successful there. And then they did a version in the UK earlier this year. And then in July for the International AIDS Conference that took place in Kigali, in Rwanda, they did a version.
And that’s kind of where I stepped in. I think with HIV Unwrapped, you’re drawn into the fashion first — and then the science comes. It’s just a really unique and different way of reframing the conversation about HIV. But beyond that, it’s also working with fashion students, young people, and to see them become so invested in HIV science. That’s what gets me the most excited. Because you’re opening a whole new world to a person who doesn’t maybe really think about HIV all that much, and now they’ve learned all this amazing stuff. Suddenly you’ve got a whole new bunch of people talking about HIV in exciting and fresh ways, and they’re telling their friends and they’re having conversations about it.
You’re trying to create different entry points for people to not only talk about the science behind HIV and AIDS, but also how we can reinterpret it in original and visually interesting ways.
I mean, look, you’ve got the House Appropriations Committee willing to advance this “Big Beautiful Bill” that slashes $2 billion in HIV funding in this country, and as someone living with HIV, you keep going, “Why would they do that? Why? We are so close to ending HIV.” All of a sudden, we’ve stopped funding research, and we’re stopping this, and I’m just like, “Why?”
Now more than ever, we’ve got people and politicians and government and a large part of the United States who think, “Oh yeah, HIV isn’t a thing anymore. It’s not important.” Well, it is still a thing. It is still important, and HIV Unwrapped is a way to be creative and open new avenues of dialogue.
A friend of mine sent me a handwritten note the other day. This is in Texas. One of his roommates wrote a handwritten note to another roommate, saying, “Oh, just so you know, ‘such and such’ has AIDS. So I’d be scrubbing the shower if I were you after he uses it. I personally have decided to go and shower at the gym.” And this is a person in their 30s, so we’re still having these dumb conversations from 1984.
That’s why I do what I do with Plus Life, and that’s why I’m like, “Wow, HIV Unwrapped is another tool in our toolbox we can use.” And I guess our hope is really that scientists will see this across the country and around the world and go, “Well, that is a really cool way to explain my science and make it accessible,” and want to engage in future projects like this.
How queer communities are represented in the media can leave deep imprints. I was watching an older interview you did where you recall this HIV ad you saw in a movie theater as a kid. The Grim Reaper’s there, and it’s creepy and sinister. It seems like we’ve moved away from that kind of imagery — but it doesn’t feel like we’ve necessarily come to a much better understanding of HIV/AIDS. Where do you think we’re at now in terms of representation?
The fact that, to this day, I can tell you where I was, what the movie was, that it was a Saturday, which cinema it was in, and I was a seven year old kid. It gives you an idea of how burned into my memory that is. And, I agree. I think we’ve moved away largely from the fear tactics, but we’ve stopped talking about it. I’d like to think that we’ve gotten better in representing people living with HIV, on television and film, as just people living with HIV. Where HIV doesn’t become the central storyline, and it’s not a doom and gloom, “woe is me” story. It’s just part of who they are.
But we sort of dance around anything that’s to do with our bodies or sex or sexuality, because it makes us uncomfortable. And so when I pitch stories to ABC and other networks, and even, quite frankly, trying to get press to cover HIV Unwrapped: we get passed on. People don’t want to talk to us because HIV isn’t sexy. As long as we keep doing that and having that reaction — if we don’t talk about it — we don’t get to a place where we can be comfortable with it.
Since I came out about my status all those years ago, my focus has been trying to normalize the conversation. That’s how we grow, and that’s how we learn — whether it’s HIV, whether it’s politics, whether it’s anything. But if we don’t talk about it, and we sort of pretend it doesn’t exist, and then we cut funding for it, and we sort of sweep it under the rug: it ain’t going to go anywhere.
Women of color, Black and brown women, have the highest infection rates in the United States. In the south those rates keep going up and up and up, and now we’re cutting funding to testing and to counseling and to services. I’m really worried that we will end up back with AIDS wards in hospitals again, and there’s no need for it.
To bring it back to HIV Unwrapped, that’s why, if I can come up and work with an amazing group of people to tell stories and to have conversations in fresh ways, then I’m going to keep doing it — whether it’s HIV Unwrapped, whether it’s what I do on Plus Life, whether it’s a television show or whatever crazy thing I come up with next.
It feels like there’s so much watering-down in terms of conversations around sexual health, HIV and AIDS. What is the resistance that you’ve faced, and how has that resistance changed over the years?
I’ve heard, “I think what you’re doing is great. It’s just not the right time to tell the story.” Well, when is the right time to tell the story? I think so many people in America think HIV doesn’t affect them. And the reality is very different. HIV affects everybody. If not now, when? People are still dying in this country. People are afraid to get tested, and they’re living in shame. And they’re hiding what’s wrong with them because of the stigma — and that just shouldn’t be happening.
I’ve said this a million times too. You know, HIV and AIDS doesn’t kill you. That’s not what’s going to put me in the grave. But it’s the stigma. It’s the bigoted, out-of-date opinions of Congress and politicians and public figures and uneducated people who just think this is somehow some deviant, dirty “sex disease” or drug disease, and those of us who get it deserve it. And you know, television networks, especially, are in the business of making money. And to do that, they sell advertising, and so they’re worried that advertisers will turn off if you talk about this kind of stuff.
And I think it’s maybe a little bit the opposite. I think if you can find, again, engaging and interesting ways to have real conversations, I’ve certainly found that you get a very vast and wide audience of people who will chime in and may have an opinion. And again, our opinions may differ, and that’s okay, but, but as long as we’re having the conversation, the more you say it, the less scary it is.
Almost 20 years after you were first diagnosed with HIV, do you see yourself pivoting now to work more on activism? Is that something you’re trying to focus more on now at this point of your career?
I will say that I’m incredibly fortunate to have worked for as many years as I have in broadcast, and I’ve done some really amazing things, and had some phenomenal opportunities going to the Oscars and doing all those red carpets and celebrity interviews all over the world. They’re all valuable experiences that I’ve been able to build upon. But I will say that in the last sort of two years, especially, my focus has become more about Plus Life and doing these kinds of stories and these kinds of initiatives.
I am fascinated by people. I think to be a decent journalist or broadcaster, you have to have that innate curiosity. And I am deeply curious about people and people’s behavior and where they come from, and what kind of homes they grew up in, what their friends are like. It’s incredibly satisfying to me. Do I miss being on regular, scheduled programming and television? Sure. It was a fantastic platform, and there’s nothing quite like the thrill of live television for me, and that’s why I loved being in news and entertainment news.
I think as I sort of get older, and I’m no longer the young kid on the block, and I’m not so nimble with my thumbs and my forefingers when it comes to putting stuff up on social media and Tik Tok and all of that…If I’ve got an opportunity to really hone in on the stuff that I do with Plus Life, there’s nothing more rewarding than that, right?
A behind-the-scenes documentary of the U.S. debut of HIV Unwrapped will be available to stream on November 30th, just before World AIDS Day.
AIDS and HIV
Assemblymembers urge Governor Newsom to sign “lifeline” bill for HIV medication
AB 554 amends existing law that restricts access to PrEP medication
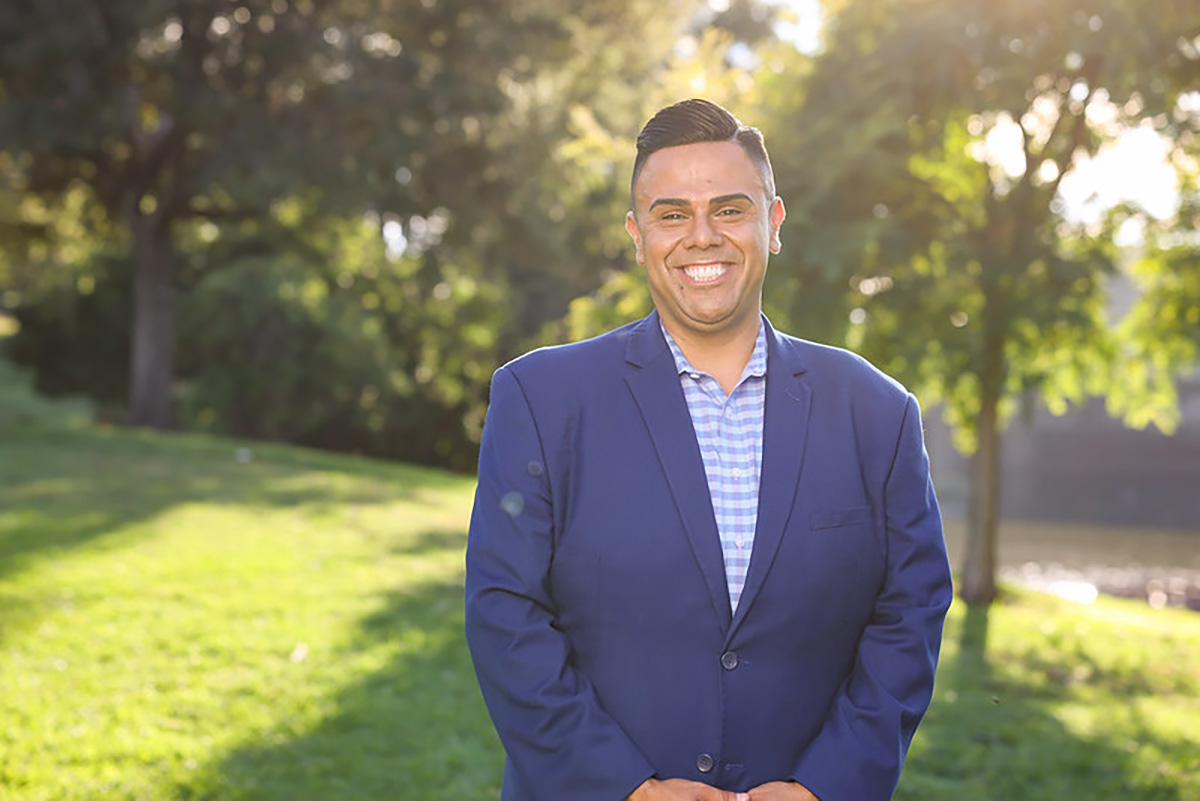

On September 10, Assembly Bill (AB) 554, or the PrEPARE Act (Protecting Rights, Expanding Prevention, and Advancing Reimbursement for Equity Act), was passed with a majority vote by the California State Assembly and Senate. Today, the bill’s leaders are urging Governor Newsom to sign it into law.
“With a powerful coalition behind AB 554, we were able to get this bill through the process swiftly, and are hopeful that the Governor will see the need for the LGBTQ+ community,” Los Angeles Assemblymember Mark Gonzalez, one of the bill’s co-authors, told the Blade.
AB 554 was first introduced in February, and was penned by Assemblymember Gonzalez and San Francisco Assemblymember Matt Haney. It was formed to amend existing laws around health insurance coverage that currently restrict access to certain antiretroviral drugs, or HIV preventative medicine like PrEP and PEP, and to ease difficulties community clinics face in administering these medications and receiving reimbursement. The bill will also require health care plans to cover FDA-approved HIV medication without enforcing prior authorization or step therapy.
For Gonzales and the bill’s supporters, AB 554 is about boosting access to various forms of effective HIV preventative medicine and providing a safeguard for people as the state of HIV research and treatment enters unsteady ground. This all comes in the midst of the debate around the House Committee on Appropriations’s 2026 Departments of Labor, Health and Human Services, and Education, and Related Agencies funding bill, which proposes $1.7 billion in cuts to domestic HIV prevention and research efforts, as well as programs that provide care for people living with HIV/AIDS — particularly, low-income people of color.
Assemblymember Gonzalez stated to the Blade that this is a “stark reminder that this epidemic still hits our communities of color the hardest,” and wants to address this by evolving and updating laws to reflect local needs. He is hopeful about the Governor’s impending response, and stated that the bill is “not just a policy; it is a lifeline.”
“It’s about giving people real choices, equipping small clinics with the tools they need to protect lives,” Gonzalez continued, “and ensuring that California continues to put public health over politics.”
AIDS and HIV
Local organization aims to support and assist Black LGBTQ+ community
REACH LA is stepping up their mission amid hostile administration

REACH LA, a Los Angeles-based nonprofit organization aimed at working with youth of color, is stepping up their prevention resources during Black History Month to support the LGBTQ+ community of color.
Though today is National Black HIV/AIDS Awareness Day, REACH LA works year-round to provide resources to their community members.
This month, the organization is amplifying its mission to support Black LGBTQ+ youth by offering free HIV testing and care throughout February, offering a $25 gift card as incentive to get tested. This and all of REACH LA’s efforts are geared toward assisting the marginalized Black and Latin American communities by reducing stigma, increasing education and assisting community members with resources.
The QTBIPOC community is especially vulnerable to political and personal attacks. As we head into the next four years under a hostile administration whose goal is to erase queer and trans people, there will be continued attacks on federal funding and on any other front possible.
“This year, it is especially vital, more than ever, to amplify and commemorate National Black HIV/AIDS Awareness Day. At REACH LA, we are currently engaging with individuals and partnerships while navigating through dire and uncertain times where HIV/AIDS awareness prevention efforts, access, and visibility have been under attack and restricted,” said Jeremiah Givens, chief marketing and communications officer at REACH LA.
It is important to spotlight the intersection between health equity, Black LGBTQ+ empowerment and community-based solutions during Black History Month and every other month throughout the year and especially during this particularly vulnerable time.
As one of eight CDC PACT Program Partners, REACH LA celebrates National Black HIV/AIDS Awareness Day with a Positive Living Campaign in collaboration with the CDC’s Let’s Stop HIV Together initiative. The campaign highlights the resilience of individuals living with HIV and works to raise awareness and foster community support.
To learn more about resources, visit their website or stop in for testing, support and other resources. The organization’s doors are open Monday through Friday, from 11 AM to 7 PM for free, on-site HIV testing and assistance with accessing PREP and PEP, linkage to care and free mental health therapy.

Over 300 people gathered last Monday to commemorate World AIDS Day in an event hosted by Bienestar Human Services. The non-profit focuses on identifying and addressing emerging health issues faced by Latinx and Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans Queer and more (LGBTQ+) populations.
The main objective of the annual event was to light a candle to honor those who passed away due to Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and celebrate those who, despite the condition, keep going.
HIV is the virus that causes Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Once you have HIV, the virus stays in the body for life, and while there is no cure. There is, however, medicine that can help people stay healthy, states Planned Parenthood. HIV destroys the cells that protect the human body from infections. If a person doesn’t have enough of these CD4 or T cells, the body can’t fight off infections as normal. This damage can lead to AIDS, which is the most serious stage of HIV, and it leads to death over time.
In the U.S., there are about 1.3 million people newly infected with HIV in 2023 and 39.9 million living with HIV, according to the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS.
Living with HIV for decades
Among the participants at the event at the Ukrainian Culture Center on Melrose in East Hollywood was Marcela, a transgender woman who was diagnosed HIV positive 33 years ago. She said when she learned about her diagnosis, she was so depressed she tried to commit suicide. She ended up at the hospital, and after getting better, she heard about an organization that was helping people with health issues such as hers.
“Since then, I learned to live with this condition because it is not an illness; it’s a condition,” she said.

Bienestar celebrated the World AIDS Day on December 2, 2024. (Courtesy of Bienestar)
Marcela, who didn’t provide her last name, said she not only found a new way of living with HIV but also found an extended family at Bienestar. They have guided her on how to receive the proper treatment and medicines, to be part of a support group and even to pay her rent when she needed it the most.
The 64-year-old woman doesn’t have any family members in the United States. She said five years ago, her husband passed away of pneumonia. She was living alone in Long Beach and got behind her payments during the pandemic. She said Bienestar helped her apply for a grant of over $20,000 that secured the payment for her rent, and now she is debt-free.
“I’m extremely grateful to them and all the help they provide,” she said.
Working for the community
This year, Bienestar is celebrating 35 years of serving the LGBTQ+ community. Among the many programs they offer is the Support Group for Transgender Women, which Marcela belongs to.
Mia Perez, the support group manager, said 15 to 20 members attend the group every Friday from 3 to 5 p.m. They talk about their feelings, share experiences, and plan and participate in social events.
Perez said one of the participants’ biggest concerns is accepting reality once they have been diagnosed. “However, with all these new treatments people that are HIV positive can have a normal relationship with someone who doesn’t have HIV. It’s all about getting informed,” said Perez.
Other concerns include what will happen to them once the new presidential administration takes office since they have plans to deport immigrants and many of the transgender women are immigrants.
“That’s why we are trying to get in contact with an immigration attorney or an organization so they can keep them informed of their rights,” said Perez.
Bienestar events, like World AIDS Day, help those affected create a stronger community, and they realize the recognition is not just for those who are HIV positive but also for their families and friends.
Marcela said when she is feeling down or bored at home, all she has to do is go to Bienestar and the people there always give her a warm welcome.
“They give me coffee, they offer me lunch. Being there is like being at home,” she said.
AIDS and HIV
New monument in West Hollywood will honor lives lost to AIDS
In 1985, WeHo sponsored one of the first awareness campaigns in the country, nationally and globally becoming a model city for the response to the epidemic

December is AIDS/HIV awareness month and this year West Hollywood is honoring the lives lost, by breaking ground on a project in West Hollywood Park that has been in the works since 2012.
Members of Hollywood’s City Council joined representatives from the Foundation of AIDS Monument to announce the commencement of the construction of STORIES: The AIDS Monument, which will memorialize 32 million lives lost. This monument, created by artist Daniel Tobin, will represent the rich history of Los Angeles where many of those afflicted with HIV/AIDS lived out their final days in support of their community.
Tobin is a co-founder and creative director of Urban Art Projects, which creates public art programs that humanize cities by embedding creativity into local communities.
The motto for the monument is posted on the website announcing the project.
“The AIDS Monument:
REMEMBERS those we lost, those who survived, the protests and vigils, the caregivers.
CELEBRATES those who step up when others step away.
EDUCATES future generations through lessons learned.”
The monument will feature a plaza with a donor wall, vertical bronze ‘traces’ with narrative text, integrated lighting resembling a candlelight vigil, and a podium facing North San Vicente Blvd.
World AIDS Day, which just passed, is on December 1st since the World Health Organization declared it an international day for global health in 1988 to honor the lives lost to HIV/AIDS.
The Foundation for the AIDS monument aims to chronicle the epidemic to be preserved for younger generations to learn the history and memorialize the voices that arose during this time.
The HIV/AIDS epidemic particularly affected people in Hollywood during the onset of the epidemic in the 1980s. The epidemic caused a devastatingly high number of deaths in the city. The city then became one of the first government entities to provide social service grants to local AIDS and HIV organizations.
In 1985, the city sponsored one of the first awareness campaigns in the country, nationally and globally becoming a model city for the response to the epidemic.
Earlier this year, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released the theme for World AIDS Day, ‘Collective Action: Sustain and Accelerate HIV Progress.’
The city of West Hollywood continues to strive to become a HIV Zero city with its current implementation of HIV Zero Initiative. The initiative embraces a vision to “Get to Zero” on many fronts: zero new infections, zero progression of HIV to AIDS, zero discrimination and zero stigma.
Along with the initiative and the new AIDS monument, the city also provides ongoing support and programming through events for World AIDS Day and the annual AIDS Memorial Walk in partnership with the Alliance for Housing and Healing.
For more information, please visit www.weho.org/services/human-services/hiv-aids-resources.
AIDS and HIV
National Latino AIDS Awareness Day: Breaking down stigma, silence and silos
FLAS provides HIV and STD education
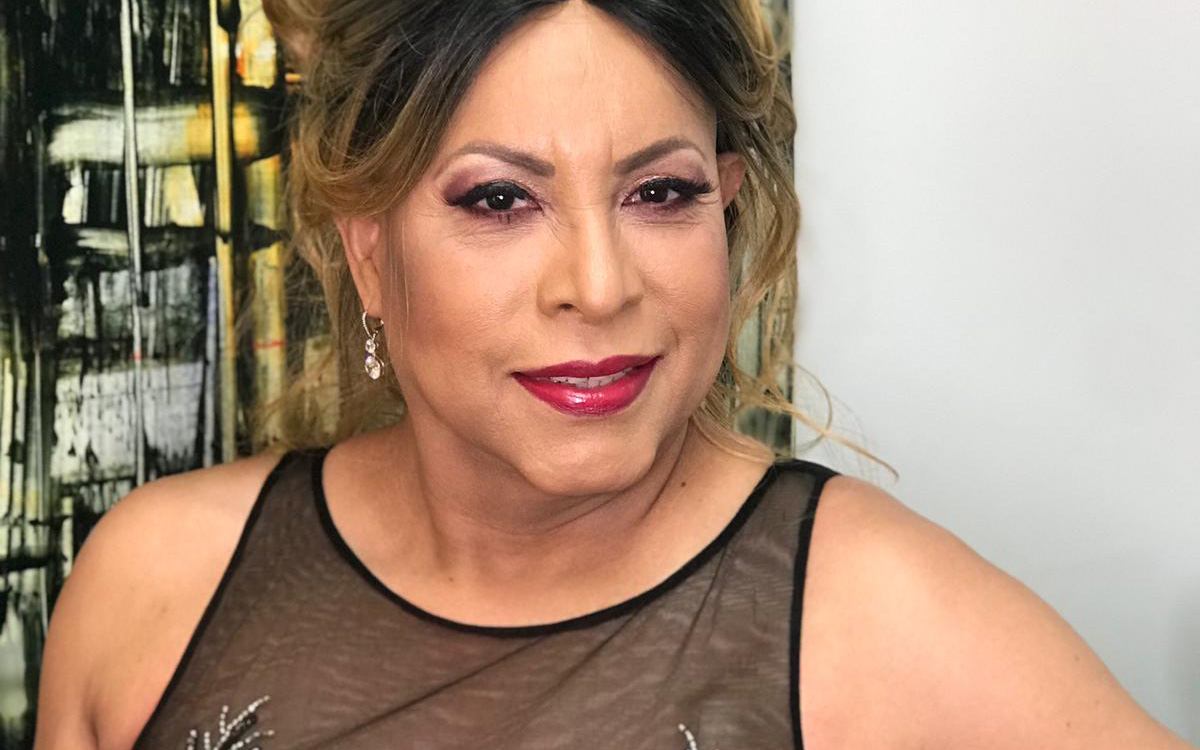

When Elia Chino, Founder and Executive Director of the Fundacion Latinoamericana De Acción Social (FLAS) Inc., initially approached major HIV/AIDS agencies in Houston, Texas for support in starting an organization tailored specifically to reaching Latino populations, she was met with confusion.
“Why do you want to start a separate organization?” they asked. “We’re here!”
Chino remembers her frustration. “They didn’t understand,” she said. “Our brothers and sisters were dying, and the community needed services that they couldn’t provide.”
Indeed, in the 1990s, barriers to HIV care and treatment for Latino populations were markedly different from those faced by other populations. Information about the HIV epidemic was largely in English, and inaccessible to many individuals who had immigrated from indigenous Latin American communities and never learned to read and write in their native language, let alone English. When they were able to access treatment, Latino individuals often faced mistreatment at primary care facilities due to a lack of culturally competent care.
Perhaps most challenging was the culture of silence. Many Latino immigrants living with HIV in the United States fled homophobia, transphobia and stigma in their home countries, and were still grappling with lasting shame and guilt. Despite many people dying, there was little open discussion or education about the cause. In fact, Chino didn’t even know that the HIV epidemic took the lives of some of her best friends until speaking with their families years later.
“No one was talking about their diagnosis,” says Chino. “People had come to the United States for freedom, but still weren’t ready to talk about who they were. There was a real atmosphere of stigma, taboo, misinformation and fear.”
At the time, Chino was volunteering at a hospital serving communities without insurance. The fourth, fifth and sixth floors were all dedicated to treating people with HIV. Chino began educating herself on this crisis while she volunteered at the hospital, and founded FLAS in 1994 after discovering that the majority of HIV prevention efforts were not reaching Latino individuals.
In the beginning, without support from other organizations in the area or resources to expand, Chino was a one-woman show, conducting outreach in clubs, cantinas and bars by herself. She hadn’t anticipated the barriers she’d face as a member of the LGBTQ+ community and an immigrant. Horrible discrimination, a language barrier and intense HIV stigma in the communities she was working in made the work challenging, but also emphasized the necessity of what she was doing.
Over time, with support and funding from organizations like Gilead Sciences, FLAS has been able to expand its services from solely HIV prevention to include HIV testing, behavioral health services, housing and social services assistance, support groups and a food pantry. The organization has started hosting educational events everywhere from churches to street corners, raising awareness about HIV in the Houston community. Chino also started collaborating with the consulate of Mexico to help newcomers navigate U.S. health systems and services when they arrive in the United States. Next year, the organization will start offering mobile HIV testing clinics for communities in need.
Since its launch, FLAS has been able to expand its initial focus to address the holistic drivers of this crisis, moving beyond medical determinants of health to tackle the social and structural barriers that perpetuate the HIV epidemic and prevent Latino populations from accessing comprehensive treatment.
“Everyone keeps telling Latino individuals to get tested, but this does nothing unless you actually incentivize people to do so,” says Chino. “People have to go to work. They have to pay their rent. They have to buy food. Many can’t afford to lose their salary and spend a full day coming in to do a test or get treatment. We have to make it easier to access HIV prevention and treatment, and we have to provide incentives.”
This year marked FLAS’s 30th anniversary, which the organization celebrated with a gala in August. They have made a huge impact in Houston since their launch – providing HIV and STD education to over 500,000 Latino people, distributing over 20,000 HIV tests, referring over 40,000 people for social services and hosting over 6,000 educational events and health fairs in English and Spanish. However, many of the challenges for HIV prevention and treatment for Latino populations remain.
“We have over 30,000 individuals living with HIV in Houston, yet when we ask for people to talk about their status, no one comes forward to tell their stories. HIV is a chronic disease, but stigmatization is still so strong in the Latino community,” says Chino. “You can say you have cancer, high blood pressure, diabetes, whatever – but nobody says I have HIV. There is still so much work to do.”
As a testament to their important programming, FLAS is a recipient of funding through Gilead Sciences’ TRANScend® Community Impact Fund, a program aimed at empowering Trans-led organizations working to improve the safety, health and wellness of the Transgender community. Since its inception in 2019, TRANScend has awarded more than $9.2 million in grants to 26 community organizations across 15 U.S. states and territories.
TRANScend support has been critical to helping FLAS maintain its services. In 2020, in the midst of the COVID pandemic, Gilead’s funding helped FLAS continue to offer virtual behavioral and mental health services to the community when their physical offices had to close.
According to Chino, this type of partnership is critical to ending the HIV epidemic in Latino communities, especially for meeting communities where they are.
“Communities trust their grassroots organizations, and grassroots organizations provide for their communities,” she says. “At the end of the day, we need to continue to support the groups doing the difficult work on the ground with the people they’re serving, especially those breaking down stigma and lasting barriers to care for Latino communities.”
AIDS and HIV
40th anniversary AIDS Walk happening this weekend in West Hollywood
AIDS Project Los Angeles Health will gather in West Hollywood Park to kick off 40th anniversary celebration
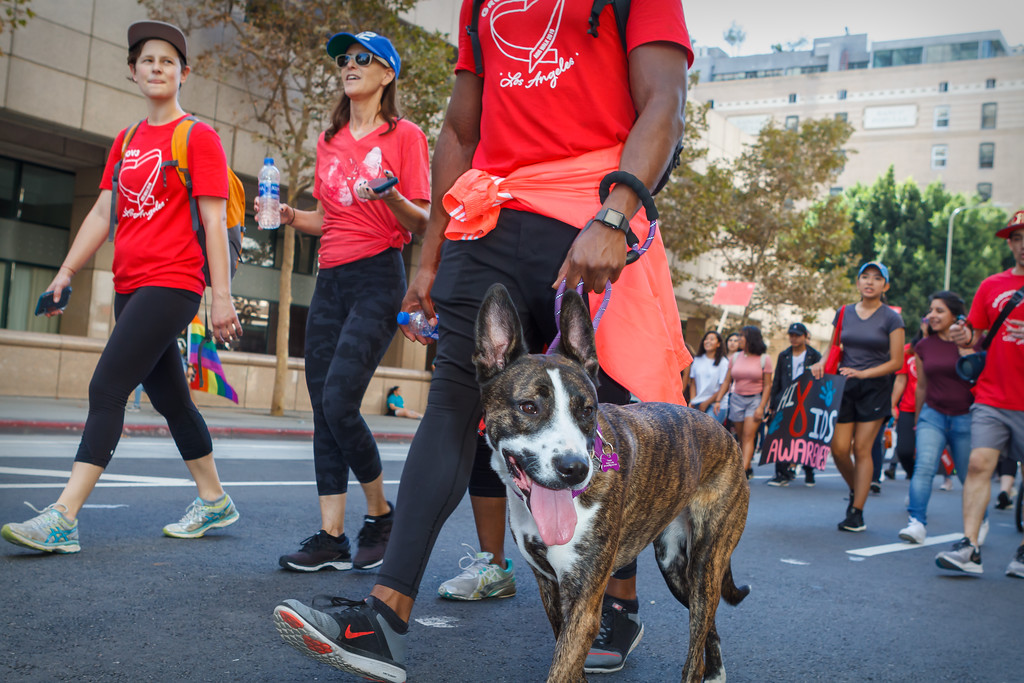

APLA Health will celebrate its 40th anniversary this Sunday at West Hollywood Park, by kicking off the world’s first and oldest AIDS walk with a special appearance by Salina Estitties, live entertainment, and speeches.
APLA Health, which was formerly known as AIDS Project Los Angeles, serves the underserved LGBTQ+ communities of Los Angeles by providing them with resources.
“We are steadfast in our efforts to end the HIV epidemic in our lifetime. Through the use of tools like PrEP and PEP, the science of ‘undetectable equals intransmissible,’ and our working to ensure broad access to LGTBQ+ empowering healthcare, we can make a real step forward in the fight to end this disease,” said APLA Health’s chief executive officer, Craig E. Thompson.
For 40 years, APLA Health has spearheaded programs, facilitated healthcare check-ups and provided other essential services to nearly 20,000 members of the LGBTQ+ community annually in Los Angeles, regardless of their ability to pay.
APLA Health provides LGBTQ+ primary care, dental care, behavioral healthcare, HIV specialty care, and other support services for housing and nutritional needs.
The AIDS Walk will begin at 10AM and registrations are open for teams and solo walkers. More information can be found on the APLA Health’s website.
AIDS and HIV
Cautious Optimism in San Francisco as New Cases of HIV in Latinos Decrease
The decrease could mark the first time in five years that Latinos haven’t accounted for the largest number of new cases
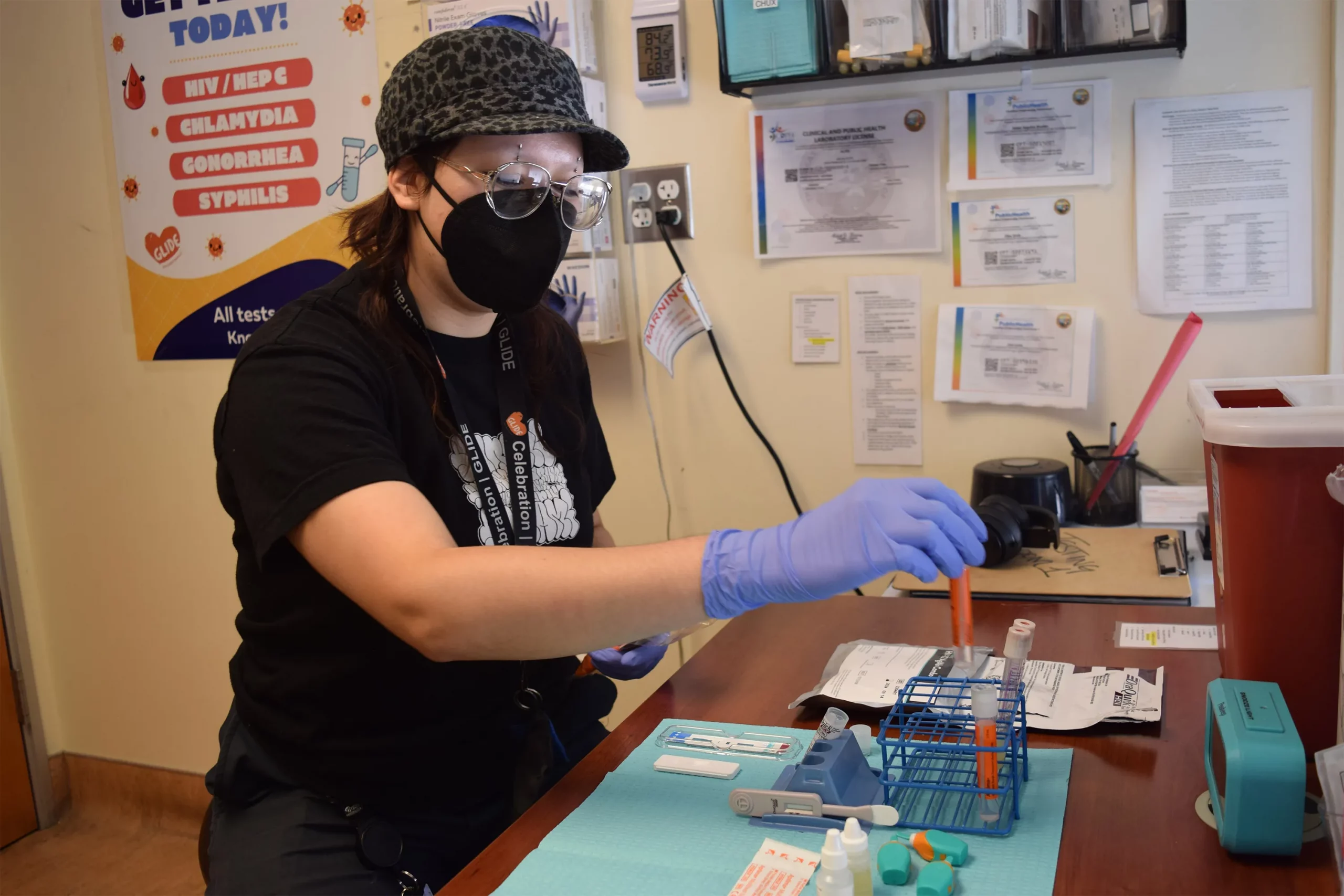
SAN FRANCISCO — For years, Latinos represented the biggest share of new HIV cases in this city, but testing data suggests the tide may be turning.
The number of Latinos newly testing positive for HIV dropped 46% from 2022 to 2023, according to a preliminary report released in July by the San Francisco Department of Public Health.
The decrease could mark the first time in five years that Latinos haven’t accounted for the largest number of new cases, leading to cautious optimism that the millions of dollars the city has spent to remedy the troubling disparity is working. But outreach workers and health care providers say that work still needs to be done to prevent, and to test, for HIV, especially among new immigrants.
“I am very hopeful, but that doesn’t mean that we’re going to let up in any way on our efforts,” said Stephanie Cohen, who is the medical director of the city’s HIV and STI prevention division.
Public health experts said the city’s latest report could be encouraging, but that more data is needed to know whether San Francisco has addressed inequities in its HIV services. For instance, it’s still unclear how many Latinos were tested or if the number of Latinos exposed to the virus had also fallen — key health metrics the public health department declined to provide to KFF Health News. Testing rates are also below pre-pandemic levels, according to the city.
“If there are fewer Latinos being reached by testing efforts despite a need, that points to a serious challenge to addressing HIV,” said Lindsey Dawson, the associate director of HIV Policy and director of LGBTQ Health Policy at KFF, a health information nonprofit that includes KFF Health News.
San Francisco, like the rest of the country, suffers major disparities in diagnosis rates for Latinos and people of color. Outreach workers say that recent immigrants are more vulnerable to infectious diseases because they don’t know where to get tested or have a hard time navigating the health care system.
In 2022, Latinos represented 44% of new HIV cases in San Francisco, even though they accounted for only 15% of the population. Latinos’ share of new cases fell to 30% last year, while whites accounted for the largest share of new cases at 36%, according to the new report.
Cohen acknowledged a one-year decline is not enough to draw a trend, but she said targeted funding to community-based organizations may have helped lower HIV cases among Latinos. A final report is expected in the fall.
Most cities primarily depend on federal dollars to pay for HIV services, but San Francisco has an ambitious target to be the first U.S. city to eliminate HIV, and roughly half of its $44 million HIV/AIDS budget last year came from city coffers. By comparison, New Orleans, which has similar HIV rates, kicked in only $22,000 of its $13 million overall HIV/AIDS budget, according to that city’s health department.
As part of an effort to address HIV disparities among LGBTQ+ communities and people of color, San Francisco last year gave $2.1 million to three nonprofits — Instituto Familiar de la Raza, Mission Neighborhood Health Center, and San Francisco AIDS Foundation — to bolster outreach, testing, and treatment among Latinos, according to the city’s 2023 budget.
At Instituto Familiar de la Raza, which administers the contract, the funding has helped pay for HIV testing, prevention, treatment, outreach events, counseling, and immigration legal services, said Claudia Cabrera-Lara, director of the HIV program at Sí a la Vida. But ongoing funding isn’t guaranteed.
“We live with the anxiety of not knowing what is going to happen,” she said.
The public health department has commissioned a $150,000 project with Instituto Familiar de la Raza to determine how Latinos are contracting HIV, who is most at risk, and what health gaps remain. The results are expected in September.
“It could help us shape, pivot, and grow our programs in a way that makes them as effective as possible,” Cohen said.
The center of the HIV epidemic in the mid-1980s, San Francisco set a national model for response to the disease after building a network of HIV services for residents to get free or low-cost HIV testing, as well as treatment, regardless of health insurance or immigration status.
Although city testing data showed that new cases among Latinos declined last year, outreach workers are seeing the opposite. They say they are encountering more Latinos diagnosed with HIV while they struggle to get out information about testing and prevention — such as taking preventive medications like PrEP — especially among the young and gay immigrant communities.
San Francisco’s 2022 epidemiological data shows that 95 of the 213 people diagnosed at an advanced stage of the virus were foreign-born. And the diagnosis rate among Latino men was four times as high as the rate for white men, and 1.2 times that of Black men.
“It’s a tragedy,” said Carina Marquez, associate professor of medicine in the Division of HIV, Infectious Diseases, and Global Medicine at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, the city’s largest provider of HIV care. “We have such great tools to prevent HIV and to treat HIV, but we are seeing this big disparity.”
Because Latinos are the ethnicity least likely to receive care in San Francisco, outreach workers want the city to increase funding to continue to reduce HIV disparities.
The San Francisco AIDS Foundation, for instance, would like more bilingual sexual health outreach workers; it currently has four, to cover areas where Latinos have recently settled, said Jorge Zepeda, its director of Latine Health Services.
At Mission Neighborhood Health Center, which runs Clinica Esperanza, one of the largest providers of HIV care to Latinos and immigrants, the number of patients seeking treatment has jumped from about two a month to around 16 a month.
Among the challenges is getting patients connected to mental health and substance abuse bilingual services crucial to retaining them in HIV care, said Luis Carlos Ruiz Perez, the clinic’s HIV medical case manager. The clinic wants to advertise its testing and treatment services more but lacks the money.
“A lot of people don’t know what resources are available. Period,” said Liz Oates, a health systems navigator from Glide Foundation, who works on HIV prevention and testing. “So where do you start when nobody’s engaging you?”
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
-

 Health3 days ago
Health3 days agoSurviving the chaos: A grounding guide for the LGBTQ community
-

 U.S. Supreme Court18 hours ago
U.S. Supreme Court18 hours agoSupreme Court hears arguments in two critical cases on trans sports bans
-

 West Hollywood21 hours ago
West Hollywood21 hours agoJohn Heilman and Danny Hang will serve as WeHo’s new Mayor and Vice Mayor
-

 Books4 days ago
Books4 days agoFeminist fiction fans will love ‘Bog Queen’
-

 Recovery3 days ago
Recovery3 days agoSobriety isn’t a punishment, it’s a power move
-

 Movies4 days ago
Movies4 days agoA Shakespearean tragedy comes to life in exquisite ‘Hamnet’
-

 Commentary5 days ago
Commentary5 days agoTrump’s triple X testosterone crusade to capture the Western Hemisphere
-

 Golden Globe Awards2 days ago
Golden Globe Awards2 days agoWanda Sykes thanking the trans community, Hudson Williams and Connor Storrie presenting, and more Golden Globes highlights
-

 COMMENTARY2 days ago
COMMENTARY2 days agoIf you’re exhausted from dating in 2025, this is how you restart for 2026
-

 Health21 hours ago
Health21 hours agoPsychedelics, sobriety, and belonging








