Money
The LGBTQ generational wealth gap
Family rejection, inheritance exclusion contribute to problems

It’s no secret that LGBTQ+ people face a range of financial challenges that heterosexual people simply don’t need to contend with. Less discussed are the effects of financial discrimination on building LGBTQ+ generational wealth. The stereotypical view of a wealthy gay couple with no children and a sizable disposable income is just that — a stereotype.
In reality, the “American Dream”— buying a home, getting married, having kids, finding a good job and investing in a 401(k) — is out of reach for many LGBTQ+ people, according to a survey by TD Ameritrade. Almost two thirds (35 percent) of LGBTQ+ millennials say they are unlikely to achieve these goals by age 40, compared to fewer than half of straight millennials. The same survey found that while the average annual income for a straight household is $79,400, the average LGBTQ+ household earns just $66,200 a year.
LGBTQ+ people are being left out of generational wealth for many reasons including family rejection, systematic barriers and a lack of financial education. With almost half of LGBTQ+ adults saying they have been excluded by a family member or close friend as a result of their sexual orientation or gender identity, according to a study by the Pew Research Center, a lack of familial financial support is a common problem for many in the community.
This combination of unique financial barriers that LGBTQ+ people face is what has led to generational wealth gap. It’s a problem that will only affect more queer people if we don’t address it now.
Legacy financial exclusion
At every stage of life, it’s not uncommon for LGBTQ+ people to encounter financial challenges that their heterosexual counterparts won’t face. Being kicked out of their homes as teens due to unaccepting parents, not receiving financial support from family for college, being removed from an inheritance — the financial cost of being LGBTQ+ can be substantial.
With the average inheritance reaching close to $177,000 according to a HSBC survey and Cerulli Associates forecasting that up to $68 trillion will trickle down to younger generations within 25 years, LGBTQ+ heirs could collectively lose trillions through inheritance exclusion.
“Even much smaller amounts could help folks pay off debt, pay off a home, send their own kids to college and help them with their own retirement. Many LGBTQ+ kids aren’t getting these benefits,” explains John Auten-Schneider. Auten-Schneider is the co-owner of The Debt Free Guys blog and host of the Queer Money podcast, a leading gay money blog and podcast for the LGBTQ+ community run by him and his husband, David.
Raising a deposit for a house or apartment can be a difficult task for all people, but without financial support from family, many would not be able to fund a deposit. When David’s parents pass away, David’s sister will likely be inheriting upwards of $1,000,000. Yet, David says, he won’t receive any of this money, solely because he’s gay. “His parents have every right to do with their money what they want, but it’s a particular disappointment that they’ll do this only because he’s gay. This, of course, means we need to plan differently for our retirement than his sister does,” explains John.
Just because David and John are LGBTQ+ financial experts doesn’t mean they don’t deal with many of the same systematic challenges that impact other members of the community. Younger LGBTQ+ people also face challenges directly related to their sexuality or gender identity.
A disproportionately high number of young people experiencing homelessness identify as members of the LGBTQ+ community. According to research from the Williams Institute, between 20 percent and 45 percent of homeless youth identify as LGBTQ+. Lacking access to basic housing or financial support from family can set up a young person up for economic disadvantage before they even graduate from high school.
LGBTQ+ students also shoulder a larger student debt burden than their straight peers to the tune of an extra $16,000. “This has been attributed, in part, to LGBTQ+ college students assuming more debt simply to leave hostile home lives. In some cases, parents may forgo helping their queer children in favor of helping their straight children,” explains John.
Knowledge is power
At the start of 2020, Michigan-based Lexa VanDamme was at her financial rock bottom. Stuck at work after a 70-plus hour work week with no money in her bank account, bills due the next day and a broken down car, she decided to make a change. “I realized that I needed to face my financial situation,” says VanDamme. “I dove deep into the online world of personal finance to learn about budgeting, debt payoff methods, saving and investing.”
After her crash course in finance, VanDamme refinanced her credit card debt into a lower-rate personal loan, created a workable budget and started a side hustle to make extra income. There were a few bumps on her journey: “I actually cycled back into credit card debt three different times. I would pay it off, then eventually max it out a few months later,” says VanDamme. Still, she managed to pay off her debt by following the financial rules she had set for herself.
While trying to learn about personal finance on her own, VanDamme realized there was a need for accessible and relatable content that appealed to a wide range of people. She decided to create The Avocado Toast Budget (The ATB). Starting out as a blog just over a year ago, The ATB now counts more than 400,000 followers on Tiktok.
“For the longest time, the loudest voices in the personal finance community were cis, straight white males and, as a queer woman, I wanted to share information and tips that were often overlooked by those creators,” says VanDamme.
For many LGBTQ+ people like VanDamme, after spending so long hiding who she really was, she wanted to live as true to herself and be as free as possible. “This led to me ignoring my spending habits and being stuck in the paycheck-to-paycheck cycle. Airing my financial dirty laundry brought up similar feelings of anxiety and concern I felt when first coming out. How would people react? What would they think?” says VanDamme.
There is already a heavy stigma around talking about personal finances, especially when you may be struggling financially. “Since queer people often spend our lives fighting for the world to accept us and our queerness, we may be less apt to talk about our financial insecurities and struggles,” says VanDamme.
Genuine representation goes beyond just diversifying the financial content creators who receive media platforms, with the advice given by these experts also needing to be fully inclusive. “Advice tended to ignore how systems of oppression affect people of color, women, the LGBTQ+ community and more. We know statistically that it’s easier for some to build wealth than others,” she adds.
VanDamme has an ongoing series on Instagram focused on the intersectional nature of many financial issues. The series helps shed some light on the economic realities that often contributes to minority community challenges. From financial inequality that disproportionately impacts disabled people to wealth inequity and racism and the cycle of poverty, VanDamme works to educate her audience on pressing topics that matter to them.
“It’s especially important to talk about the financial challenges that trans people in our community face. This includes increased reports of lower wages, limited and more expensive housing options, and twice the rate of unemployment. This heavily impacts their ability to build wealth,” she explains.
Intersectional challenges
While being LGBTQ+ can underpin unique money issues, queer people of color and queer women often experience additional difficulties around financial matters.
In addition to the financial barriers faced by LGBTQ+ people, queer people of color also face a racial wealth gap. Employment discrimination, systematic inequalities and disparities in financial education all contribute to this unequal financial playing field.
According to research from the Federal Reserve, the average white family’s wealth is eight times higher than the wealth of an average Black family. The gender pay gap also contributes to excluding women from building generational wealth, according to the latest statistics compiled by Pew Research, which show that women earned 84 percent of what men earned in 2020.
Carmen Perez, creator of Make Real Cents, a personal finance blog dedicated to helping people achieve financial independence, believes it’s important to have experts who are more representative of the people they’re speaking to. “I heard a quote a while ago: ‘You can’t be what you can’t see.’ I think that’s really important because eventually, if you don’t have a model to follow, either you have to be the first, or it’s never going to happen,” she says.
As a woman of color and a lesbian, Perez knows firsthand how important it is to address the absence of representation in financial education. “It’s definitely one of the things we have to step back and look at in the LGBT community,” says Perez. “There’s a compounding effect because not only am I part of the LGBT community as a lesbian, but I’m also a minority, and I’m also a woman, and there’s a lot of hurdles up against a lot of folks in this space,” she adds.
With more than 60,000 people following her Make Real Cents account, Perez is playing a part in democratizing access to finance. There, she does everything from break down the cost of credit to explain 401(k) company matches with easy-to-read graphics and Insta stories. Her methods are a world away from the complexity of some traditional financial advisors and tools.
“Millennials are starting to change the money game because we’re delivering advice in a way that isn’t super technical. It can be so overwhelming to watch CNBC with all these screens and tickers that don’t mean anything to you personally,” says Perez.
Increased representation in the finance space means a light can be shone on vital issues, resulting in deeper conversations that make money less taboo. “We’re finding instances where historically people who have been locked out of the finance industry, by design, are speaking up. Unlike some traditional financial advisors that give out all this jargon and talk in all these terms that many may not understand,” says Perez.
Future generations
Despite the long-standing barriers facing LGBTQ+ people in gaining access to financial education and financial services, LGBTQ+ personal finance content creators now offer a way for many to improve their financial literacy in more convenient ways than ever before. While investing early and regularly is one of the most effective ways to secure a financially comfortable retirement, it’s never too late to build wealth and support for the next generation of LGBTQ+ people.
“[You can] create legacy wealth within the LGBTQ+ community by setting up your estate plan to donate to LGBTQ+ causes that will help homeless youth and [by] giving to local, younger LGBTQ+ folks you know personally,” adds John.
Negotiating the LGBTQ+ generational wealth gap is no small feat. But continuing the discussion around both financial literacy and taking steps to combat systematic financial issues can go a long way to address the financial challenges impacting the LGBTQ+ community.
“The stronger we are as LGBTQ+ individuals and allies, including our financial strength, the stronger we are as a community,” concludes John.

Finbarr Toesland is an award-winning journalist committed to illuminating vital LGBTQ+ stories and underreported issues. His journalism has been published by NBC News, BBC, Reuters, VICE, HuffPost, and The Telegraph.

Money
Sweeping changes for electricity bills: Earn more pay more planned
California’s utilities proposed charging customers based on income in new rate plans submitted to the Public Utilities Commission

SACRAMENTO – In a joint proposal to the state’s Public Utilities Commission, California’s three largest power companies, Southern California Edison, Pacific Gas & Electric, and San Diego Gas & Electric, have put forth a sweeping change to how customers pay for their electrical power.
California’s utilities proposed charging customers based on income in new rate plans submitted to the Public Utilities Commission. The proposal follows last year’s passage of Assembly Bill 205 which requires a fixed rate and generally simpler bills.
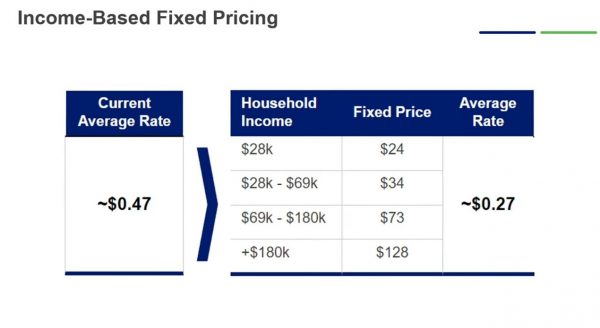
Under the proposal:
- Households earning less than $28,000 a year would pay a fixed charge of $15 a month on their electric bills in Edison and PG&E territories and $24 a month in SDG&E territory.
- Households with annual income from $28,000 – $69,000 would pay $20 a month in Edison territory, $34 a month in SDG&E territory and $30 a month in PG&E territory.
- Households earning from $69,000 – $180,000 would pay $51 a month in Edison and PG&E territories and $73 a month in SDG&E territory.
- Those with incomes above $180,000 would pay $85 a month in Edison territory, $128 a month in SDG&E territory and $92 a month in PG&E territory.
San Diego Gas & Electric CEO Caroline Winn said in a statement: “We have listened to and heard from our customers that fundamental change is needed to provide bill relief. When we were putting together the reform proposal, front and center in our mind were customers who live paycheck to paycheck, who struggle to pay for essentials such as, energy, housing and food.”
The electric pricing reform proposal is a central to improve affordability for customers, which also includes:
- Pursuing federal funds available through the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act to pay for critical electric infrastructure, and maximizing federal tax credits for battery storage and microgrid facilities that can be refunded to customers;
- Advocating for legislation (AB 982) to remove costs from electric rates that could reduce monthly bills up to 7% and legislation (AB 1513) to spread the cost of wildfire safety improvements over a longer period of time to reduce rate impacts;
- Stabilizing natural gas bills by advocating for improved utilization of existing infrastructure
A chorus of voices, including nonpartisan research organizations such as Next 10, energy experts such as UC Berkeley’s Severin Borenstein, and environmental groups such as the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) have called for this type of reform to make electricity more affordable and support the state’s clean energy transition.
State law requires the CPUC to adopt a new rate structure by July 1, 2024. Southern California Edison says the earliest customers would see the updated bills is 2025
California utilities propose charging customers based on income:
SDG&E proposes billing electricity customers based on income:
Money
FBI warns of QR code scam
Practice caution when entering financial information as well as providing payment through a site navigated to through a QR code

WASHINGTON – The Federal Bureau of Investigation’s cybercrimes division issued a warning to consumers and others this week that cybercriminals are targeting Quick Response codes in an effort to steal financial and other personal information.
A QR code is a square barcode that a smartphone camera can scan and read to provide quick access to a website, to prompt the download of an application, and to direct payment to an intended recipient. Businesses use QR codes legitimately to provide convenient contactless access and have used them more frequently during the COVID-19 pandemic, the FBI noted in a bulletin issued Tuesday.
However, cybercriminals are taking advantage of this technology by directing QR code scans to malicious sites to steal victim data, embedding malware to gain access to the victim’s device, and redirecting payment for cybercriminal use the FBI added.
Cybercriminals tamper with both digital and physical QR codes to replace legitimate codes with malicious codes. A victim scans what they think to be a legitimate code but the tampered code directs victims to a malicious site, which prompts them to enter login and financial information. Access to this victim information gives the cybercriminal the ability to potentially steal funds through victim accounts.
Malicious QR codes may also contain embedded malware, allowing a criminal to gain access to the victim’s mobile device and steal the victim’s location as well as personal and financial information. The cybercriminal can leverage the stolen financial information to withdraw funds from victim accounts.
Businesses and individuals also use QR codes to facilitate payment. A business provides customers with a QR code directing them to a site where they can complete a payment transaction. However, a cybercriminal can replace the intended code with a tampered QR code and redirect the sender’s payment for cybercriminal use.
While QR codes are not malicious in nature, it is important to practice caution when entering financial information as well as providing payment through a site navigated to through a QR code. Law enforcement cannot guarantee the recovery of lost funds after transfer.
TIPS TO PROTECT YOURSELF:
- Once you scan a QR code, check the URL to make sure it is the intended site and looks authentic. A malicious domain name may be similar to the intended URL but with typos or a misplaced letter.
- Practice caution when entering login, personal, or financial information from a site navigated to from a QR code.
- If scanning a physical QR code, ensure the code has not been tampered with, such as with a sticker placed on top of the original code.
- Do not download an app from a QR code. Use your phone’s app store for a safer download.
- If you receive an email stating a payment failed from a company you recently made a purchase with and the company states you can only complete the payment through a QR code, call the company to verify. Locate the company’s phone number through a trusted site rather than a number provided in the email.
- Do not download a QR code scanner app. This increases your risk of downloading malware onto your device. Most phones have a built-in scanner through the camera app.
- If you receive a QR code that you believe to be from someone you know, reach out to them through a known number or address to verify that the code is from them.
- Avoid making payments through a site navigated to from a QR code. Instead, manually enter a known and trusted URL to complete the payment.
If you believe you have been a victim of stolen funds from a tampered QR code, report the fraud to your local FBI field office at www.fbi.gov/contact-us/field-offices.
The FBI also encourages victims to report fraudulent or suspicious activities to the FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center at www.ic3.gov.
-

 Crime & Justice5 days ago
Crime & Justice5 days agoEd Buck is ordered to pay $2 million in wrongful death lawsuit for Gemmel Moore
-

 GLAAD Media Awards5 days ago
GLAAD Media Awards5 days agoLiza Minnelli surprises guests at the 2026 GLAAD Awards, Laverne Cox’s fiery speech earns a standing ovation
-

 Events2 days ago
Events2 days agoCarrying the sapphic torch forward: The Dinah returns this year with new leaders
-

 a&e features4 days ago
a&e features4 days agoQuick chat: Katya Zamolodchikova works with Grindr to answer ‘Who’s the A**hole?’
-

 Best of LGBTQ LA2 days ago
Best of LGBTQ LA2 days agoThe Los Angeles Blade’s Best of LA Awards Show returns for its 9th year
-

 a&e features1 day ago
a&e features1 day agoMelvin Robert will perform homecoming solo at Gay Men’s Chorus of LA’s Spring concert
-

 GLAAD Media Awards2 days ago
GLAAD Media Awards2 days agoBill Condon, Frankie Grande, and David Archuleta reflect on queer joy in their lives at the 2026 GLAAD Media Awards
-

 Movies2 days ago
Movies2 days agoIntense doc offers transcendent treatment of queer fetish pioneer
-

 Commentary15 hours ago
Commentary15 hours agoThe fad of family estrangement: Ending connections in order to honor the ones that truly sustain us





