Monkeypox
Monkeypox outbreak debacle: “Failure to communicate & vaccinate”
“The question is when will we ever learn that a small investment in prevention & surveillance is worth a pound of cure?”
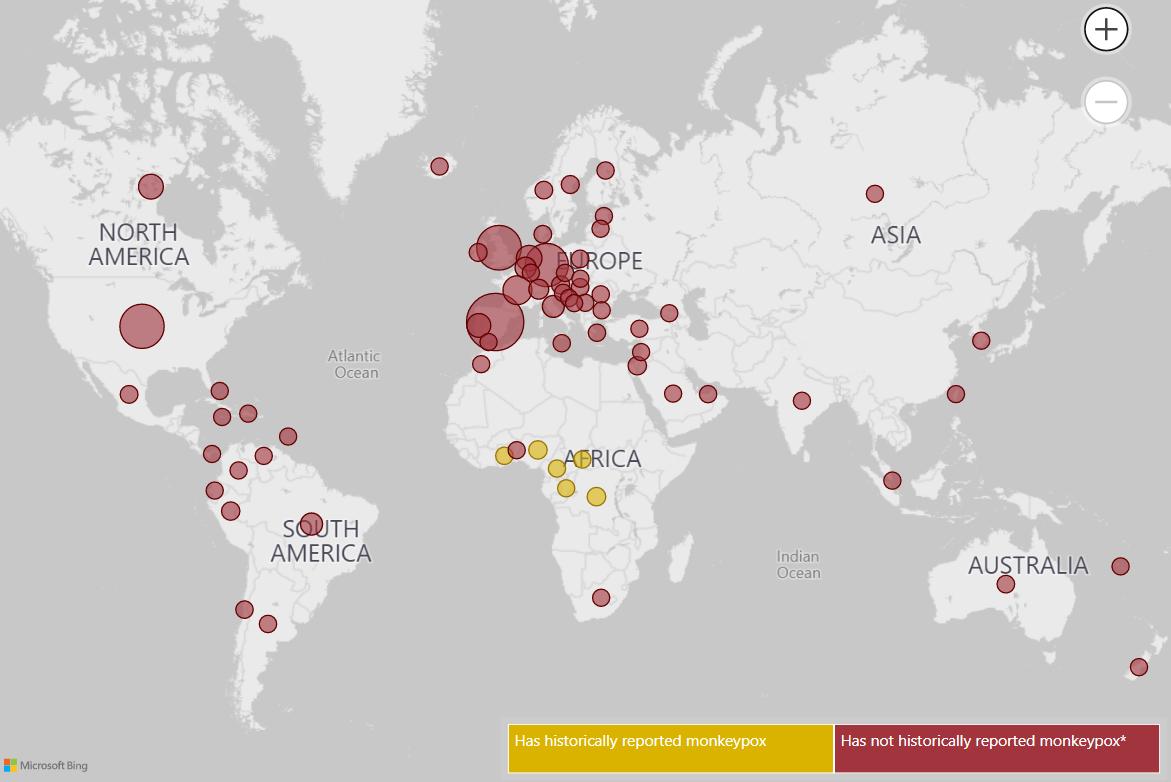
LOS ANGELES – Directly linked as the epi-centres for the outbreak of the current global Monkeypox virus, which occurred in the latter part of May this year, were a Gay Pride event in the Spanish Canary Islands, the Darklands fetish festival in Antwerp, Belgium, and raves in Berlin, Germany and Madrid, Spain.
The common denominator for all of those persons affected by the viral outbreak was that they were gay or bisexual men. The number of the first recorded cases was less than ten individuals infected per event, but since then the number has grown exponentially and spread rapidly. As of July 19, 2022 globally there are 14, 511 cases in over 70 countries according to the latest data from the World Health Organization, (WHO).
In the United States on July 19, 2022, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention‘s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases the case count was 2,108.
Leading the number of cases were New York with 581, California with 267, Illinois with 200, Florida with 180, Georgia with 132, and the District of Columbia with 126. CDC reported that the metropolitan areas of New York City, San Francisco, Los Angeles, Chicago, Miami-Dade, Atlanta plus Washington D.C. with their high concentrated populations of gay and bisexual men accounted for the majority of the case counts.
While the primary transmission is intimate bodily or personal contact such as a kiss, WHO clinical researchers were able to determine that in numerous cases in Europe the viral DNA was detected in seminal analysis defining sexual transmission as another means of infection.
The Blade communicated with Dr. David Heymann, an American infectious disease epidemiologist and public health expert, based in London, UK who was formerly Executive Director of WHO’s communicable diseases cluster. Heymann pointed out that “We know monkeypox can spread when there is close contact with the lesions of someone who is infected, and it looks like sexual contact has now amplified that transmission.”
Last week, WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus told reporters that the U.N. agency will reconvene a meeting of the committee that will advise on declaring the outbreak a global health emergency this week when it meets in Geneva, Switzerland on Thursday.
Ghebreyesus also pointed out that a lack of testing meant that there were likely many more cases going unreported. “I continue to be concerned by the scale and spread of the virus across the world,” the Director-General said.
In the U.S. CDC Director Rochelle Walensky told reporters late last week in a virtual press briefing that five commercial laboratory companies would soon begin offering monkeypox testing.
“The ability of commercial laboratories to test for monkeypox is an important pillar in our comprehensive strategy to combat this disease,” said Walensky. “This will not only increase testing capacity but also make it more convenient for providers and patients to access tests by using existing provider-to-laboratory networks.”
The CDC Director said that the Mayo Clinic Laboratories has begun testing for monkeypox using CDC’s orthopoxvirus test, which detects most non-smallpox related orthopoxviruses, including monkeypox. On Monday of this week, the CDC announced that Sonic Healthcare USA (Sonic) will also begin testing for monkeypox using CDC’s orthopoxvirus test.
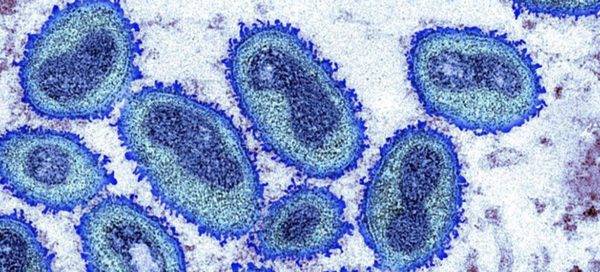
Monkeypox overview:
- Monkeypox is a viral infection that can cause a flu-like illness and characteristic rash. The pathogen that causes this infection is an Orthopoxvirus, “the same genus as the virus that causes smallpox,” according to MDH, though it is “less severe.” The rash can develop into fluid-filled bumps that eventually scab over. The illness can last three to four weeks.
- Monkeypox is a bit of a misnomer. It doesn’t mainly occur in monkeys. Rodents are the likeliest source, but the virus can leap to other species, including humans. Those who are infected can transmit it to other people. Before now, monkeypox infections have mainly occurred in some African countries.
- Severe illness can occur, but perspective is crucial. Global health officials list the case fatality ratio at 3-6%, which may reflect a lack of access to medical care in countries where monkeypox is endemic. The WHO said no deaths had been reported in the 2022 outbreak outside of Africa. In addition, the current outbreak appears to be caused by a monkeypox “clade,” or strain, less likely to cause severe illness.
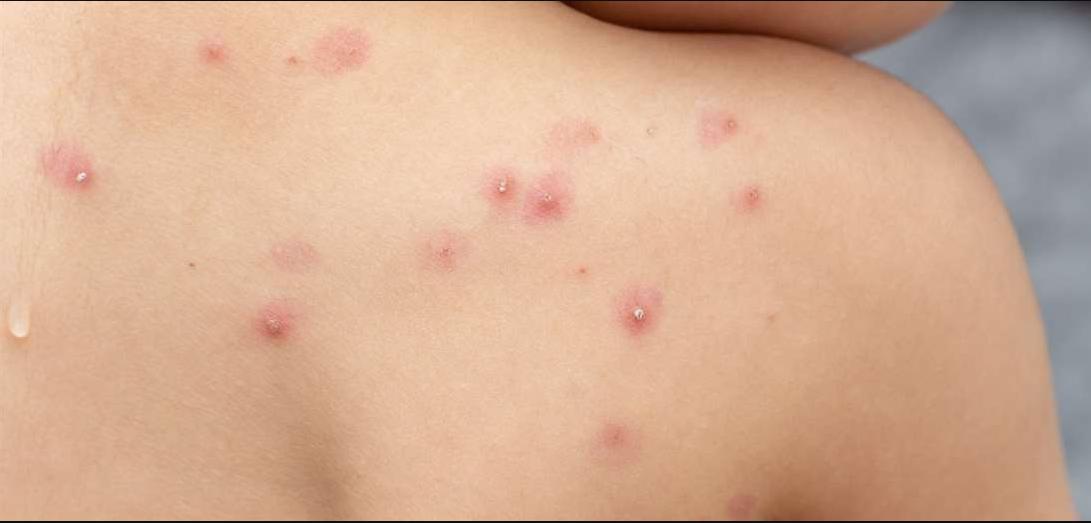
- Two critical things to know about the rash: As more people are infected, we are learning that the rash can be “very, very painful,” though, in others, it might not be very noticeable, health officials said. In addition, people remain infectious until scabs heal and healthy new skin appears. People should be off work and take other precautions until they heal.
- How monkeypox spreads in humans: “Direct contact with body fluids or skin lesions (i.e., skin-to-skin contact) is the most common mode of human-to-human transmission,” state health officials advise. “Transmission via respiratory particles can also occur but usually require prolonged face-to-face contact.” To be even clearer: Sexual activity provides a setting where this contact can occur, facilitating viral spread. Transmission can also occur if someone wears or uses an infected person’s clothing, bedding or towels. While anyone can get monkeypox, risk increases with “multiple or anonymous sex partners,” according to the CDC.
- Time frame from exposure to symptoms: Twelve days is often when people start feeling sick after becoming infected, but symptoms could appear anywhere from five days to 21 days afterward.
- A vaccine and antivirals are available: Health officials said the vaccine could “actually stop the disease” if given within four days of exposure. It can still mitigate the illness if given up to 14 days later. Prescription drugs such as TPOXX (tecovirimat) may also be beneficial.
As the outbreak rolled on in June and into early July criticism and questions begun to be raised over vaccines and testing. In New York City, an Out gay medical resident and PhD candidate Lala Tanmoy (Tom) Das noted in an op-ed written for CNN:
“The demand outpacing supply is a problem we could have prevented; demand was and is largely predictable as cases in the US are still mostly limited to men who have sex with men (MSM) — many of whom self-identify as gay, bisexual or transgender. And studies consistently show that LGBTQ individuals are much more likely to get vaccinated than our heterosexual peers — including getting the Covid-19 vaccine.”

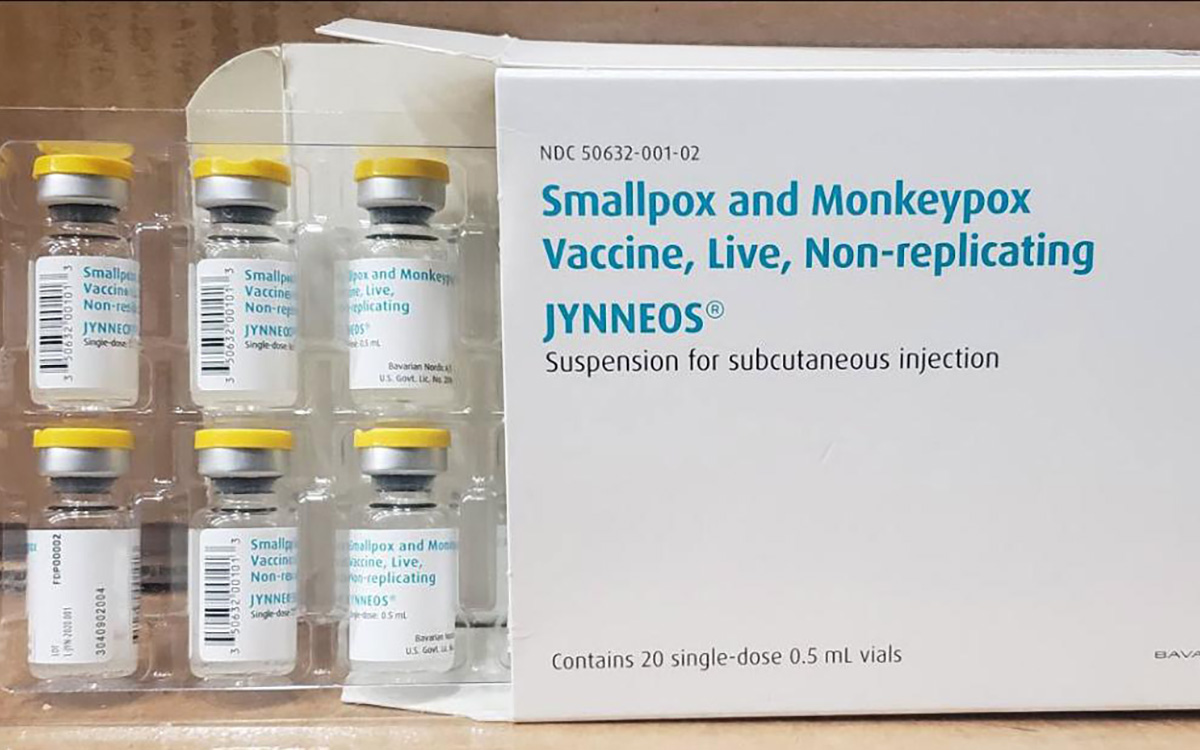
(Photo Credit: Bavarian Nordic)
The JYNNEOS Smallpox (Monkeypox) Vaccine is manufactured solely by the Danish Bavarian Nordic A/S company in Denmark. Since 2010, The company has manufactured its liquid-frozen MVA-BN smallpox vaccine and has supplied doses to the U.S. Strategic National Stockpile (SNS) for emergency use.
However there has been greater demand than supply. The United States has distributed about 156,000 monkeypox vaccine doses nationwide, including more than 100,000 doses in just the past week. The CDC Director noted “We are actively working to increase supply… update our strategy to make sure we are using our current supply strategically,” she said.
Part of the problem was that the U.S. Food & Drug Administration, (FDA) was slow in signing off on approval of a facility “We were beginning the process of pre-positioning those doses in the US, but they will be available pending the FDA clearance of the facility expected by the end of July,” Walensky said.
Political leadership was quick to point out that the Federal response was anemic and lacking impetus. California State Senator Scott Wiener blasted federal agencies over the apparent lack of preparedness and the recent lessons gained from the coronavirus pandemic.
“We need to be very clear where the responsibility lies for this completely avoidable situation: the federal government. As far back as 2010, public health experts were warning that it was inevitable that monkeypox would spread beyond West Africa. And in 2019, the FDA approved a safe and effective monkeypox vaccine. Yet, the United States government ordered a mere 56,000 vaccine doses (enough for 28,000 people) for the national vaccine stockpile and failed to order the millions of doses that should have been ordered in preparation for an inevitable outbreak. … We need an enormous amount of additional vaccine doses, and we need it immediately. The federal government’s failures are threatening to deeply harm our community. Once we move past this emergency, we need accountability for these failures — failures that put people’s lives and health in jeopardy.”
In a letter sent to U.S. Health and Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra on Tuesday, U.S. Representative Adam B. Schiff (D-CA28), who represents portions of Los Angeles including the city’s traditionally LGBTQ+ neighborhoods, expressed serious concerns regarding the federal response.
“The demand for monkeypox vaccinations across the country far outweighs supply, with members of at-risk communities reportedly being turned away at vaccination sites due to limited supply. Public health experts estimate that confirmed cases reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) vastly underrepresents the true number of cases due to limited access to testing. I am deeply concerned that the approximately 7 million doses of the JYNNEOS vaccine acquired by the United States will not meet the sky-rocketing demand,” Schiff wrote.
“The current supply of the two-dose vaccine regimen accounts for only 3.5 million residents in the United States. With some shipments of the vaccine not expected to arrive until well into 2023, the current federal vaccination strategy falls short in terms of supply and timeliness. I urge HHS, in coordination with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), to draw upon lessons learned during the Covid-19 pandemic and use the full power of the executive branch to increase manufacturing and distribution of the JYNNEOS vaccine across the country as quickly as possible.”
The other considerations being overlooked say LGBTQ+ health care advocates and political leaders are the confusing and somewhat impossible labyrinthic requirements for getting a vaccine.
There is also a lack of a unified approach to containment and prevention. Rep. Schiff warned that more needed to be done:
“I strongly encourage HHS to develop and implement a comprehensive, long-term strategy to combat the spread of the monkeypox virus in the United States. Sky-rocketing cases and limited vaccination supply world-wide suggests that the monkeypox virus will continue to spread for years to come, if not indefinitely. The HIV crisis and Covid-19 pandemic have demonstrated it is critical that public health officials be forward-thinking in combatting the spread of viral infections – particularly in instances when marginalized communities, such as the LGBTQ+ community, are hardest-hit. It is imperative that HHS consider, develop, and implement a public health strategy that will ensure access to monkeypox testing, vaccination, treatment, and provider education for years to come.”
The AIDS Healthcare Foundation’s President Michael Weinstein in a press conference last week said that “regardless of what term is used by WHO, monkeypox is a pandemic. …the effort at every level of government is failing to address it.”
Rick Zbur, the former Executive Director of Equality California also agreed with Weinstein’s assessment especially as far as the response by the Los Angeles Department of Public Health,(LADPH) in dealing with the building crisis.
“[LADPH] has been making it difficult to obtain the vaccine – let alone information. There’s no human interface just the 211 system which leads into a confusing set of menus and then nothing clearly labeled as monkeypox related,” Zbur said. ” If you do get through to a human then you may end up waiting six hours on hold- in some cases literally,” he added.
The other issue is that the LADPH has focused on its own system of clinics and appointment sites that exclude for the most part the neighborhoods of Los Angeles where the LGBTQ+ community lives- especially those most affected, gay, bisexual and Trans Angelenos.
“The people affected are in Silver Lake through Hollywood into West Hollywood and Downtown LA,” Zbur said. Yet one of the clinic locations is in Santa Clarita which is not accessible by transit systems and is a long commute, not to mention hardly a center for the LGBTQ+ population. “There aren’t walk-in clinics for testing and then there are up to 2 hour potential travel times for some LGBTQ+ people,” Zbur pointed out.
AHF’s Weinstein argued that the current monkeypox spread is part of the country’s larger failure to prevent and treat STIs, and that many individuals who test positive for monkeypox also test positive for other STIs.
“The question that I keep coming back to is when will we ever learn that a small investment in prevention and surveillance is worth a pound of cure?” Weinstein said. “We need to put the public back in public health.”
Zbur, Weinsten, and Weiner all pointed out that historically because of the HIV/AIDS pandemic the LGBTQ+ community already had the resources and clinical healthcare infrastructure in place to best serve the very community that is disproportionately affected by the outbreak.
Zbur noted that while unlike the HIV/AIDS pandemic there is a vaccine, the lackluster response by government especially that while the agencies like LADPH may see their distribution and testing as equity driven, the truth is that with the central community affected being the LGBTQ+ community their response is mismatched with the reality of the outbreak.
“This is a disruption of normal lives for our community- for entering into intimate relationships or even attending events shirtless or in a tank-top,” Zbur said. LADPH and others need to refocus and take into account our community, and more so where our community actually lives,” he added.
Eligibility and vaccine distribution also needs to be better thought out Zbur said, a point stressed by Dr. Lala Tanmoy (Tom) Dasin his op-ed to CNN.
“We also need to supplement the current approach in many cities of first-come-first-served, online-only scheduling portals with pre-registration (like Washington, DC is doing) and walk-in options. As we witnessed with the Covid-19 vaccine rollout, the online, first-come-first-served system disadvantages anyone who has work or other obligations that prevent them from getting online the minute appointments are released, as well as people with unstable housing who don’t often have access to digital technology.“
In terms of information, AHF noted:
- The Los Angeles County Department of Public Health should conduct twice weekly public briefings outlining the number of new cases and where they are occurring.
- Warnings to the gay and bisexual male population should be launched online, in newspapers and in outdoor advertising advising men to watch for symptoms; avoid group sexual situations; consult a doctor if you have symptoms indicative of monkeypox, and isolate if you are diagnosed.
- Require signs to be posted in commercial sex venues and via banner or other ads on hookup applications.
- Lobby the federal government to supply vaccine on an emergency basis.
- Regularly engage community partners to assist the Department of Public Health in prevention, testing, vaccination and treatment of monkeypox.
- Engage universities to initiate studies to determine the changed characteristics of monkeypox in the current pandemic.
On Tuesday the LADPH released its latest updates:
With the arrival of an additional 9,000 JYNNEOS doses late last week and an additional 7,000 doses arriving later this week, the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health (Public Health) is expanding eligibility for the monkeypox vaccine to include additional residents at higher risk of exposure.
Beginning tomorrow, Wednesday, July 20, monkeypox vaccine will be available for gay men, bisexual men, men having sex with men, and transgender persons who:
- Were diagnosed with gonorrhea or early syphilis within the past 12 months; or
- Are on HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP); or
- Attended or worked at a commercial sex venue or other venue where they had anonymous sex or sex with multiple partners (e.g., saunas, bathhouses, sex clubs, sex party) within past 21 days.
Residents who fall under these eligibility requirements can get vaccinated several ways:
- Contacting their doctor or healthcare provider to find out if they are a monkeypox vaccine provider. If they are a vaccine provider, eligible residents can request an appointment with their provider to get vaccinated. Providers that are registered to administered vaccine may also reach out to patients who are thought to be eligible to invite them to get vaccinated.
- Visiting a Public Monkeypox vaccine location with their ID and provide one of the following:
- Proof of gonorrhea or early syphilis infection in the last 12 months in the form of a lab report (the proof can be shown from your phone, including a screenshot of the result or within a patient portal; OR
- A monkeypox provider attestation form completed by your doctor; OR
- Being invited to get vaccinated after receiving a text message with their name from the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health.
Residents who meet any of the eligibility criteria can fill out a sign-up form by visiting ph.lacounty.gov/monkeypoxsignup and providing their name, date of birth, and eligibility information to get on a list to receive vaccine if they meet the eligibility criteria and vaccine is available. Residents can also indicate locations that are most convenient for them to get vaccinated.
Those without access to the internet or needing help with registration, can call 2-1-1 for assistance.
Public Health will continue to provide monkeypox vaccines by invitation only to the following persons identified through public health investigation, including:
- Persons confirmed by Public Health to have had high- or intermediate-risk contact with someone with monkeypox, as defined by CDC.
- Persons who attended an event or venue where there was high risk of exposure to an individual(s) with confirmed monkeypox virus through skin-to-skin or sexual contact. Public Health will work with event/venue organizers to identify persons who may have been present and at risk of exposure while at the venue.
Public Health or clinic partners will directly communicate to those identified as being close contacts to a confirmed case to provide details on how and where to access the JYNNEOS vaccine.
For more information, please visit: http://publichealth.lacounty.gov/monkeypox/
Monkeypox
US contributes more than $90 million to fight mpox outbreak in Africa
WHO and Africa CDC has declared a public health emergency
The U.S. has contributed more than $90 million to the fight against the mpox outbreak in Africa.
The U.S. Agency for International Development on Tuesday in a press release announced “up to an additional” $35 million “in emergency health assistance to bolster response efforts for the clade I mpox outbreak in Central and Eastern Africa, pending congressional notification.” The press release notes the Biden-Harris administration previously pledged more than $55 million to fight the outbreak in Congo and other African countries.
“The additional assistance announced today will enable USAID to continue working closely with affected countries, as well as regional and global health partners, to expand support and reduce the impact of this outbreak as it continues to evolve,” it reads. “USAID support includes assistance with surveillance, diagnostics, risk communication and community engagement, infection prevention and control, case management, and vaccination planning and coordination.”
The World Health Organization and the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention last week declared the outbreak a public health emergency.
The Washington Blade last week reported there are more than 17,000 suspected mpox cases across in Congo, Uganda, Kenya, Rwanda, and other African countries. The outbreak has claimed more than 500 lives, mostly in Congo.
Monkeypox
LA County Public Health gives 200 Mpox Vax at WeHo Pride
Street Fair attendees lined up for their Mpox vaccination, while others asked questions & gathered info to get their vaccine at a later date
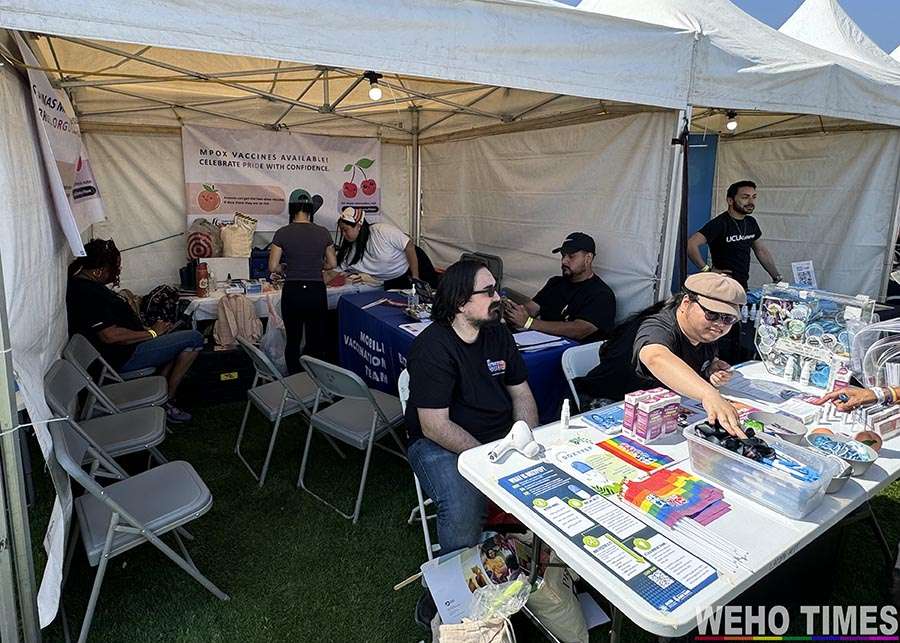

By Paulo Murillo | WEST HOLLYWOOD – The Los Angeles County Department of Public Health administered Mpox vaccinations at an on-site pop-up clinic at the WeHo Pride Street Fair during WeHo Pride Weekend on Saturday June 1, 2024 and Sunday, June 2, 2024, on Santa Monica Boulevard in the City’s Rainbow District.
According to a LA County public health nurse, 200 Mpox vaccinations were administered during the weekend. She said she believed it was an even 100 for each day, which was a much larger number than expected.
Several Street Fair attendees lined up for their mpox vaccination, while others asked questions and gathered information to get their vaccine at a later date because they didn’t want to risk feeling side effects during the pride festivities.
The Los Angeles County Department of Public Health is hitting pride events again this year and is offering the Mpox (formerly known as “monkeypox”) vaccinations for free during various pride festivals throughout LA. county. No appointment are necessary. Individuals can simply sign up and wait their turn. The LA County Public Health booth is also condoms, swag and information on COVID, STDS and more.
The mpox vaccine is currently available to anyone who requests it and individuals do not have to disclose information about personal risk. The virus spreads primarily from prolonged skin-to-skin contact, which includes hugging, sleeping in the same bed, or sexual activity, and can also be transmitted via direct contact with scabs, rashes, or respiratory secretions from a person infected with mpox.
Large gatherings can become hubs for transmission of the virus, which disproportionately affected gay men, bisexual men, and other men who have sex with men (MSM) in a breakout in 2022.
According to the Los Angeles County Mpox case summary updated every other Friday, data as of May 30, 2024 a total of 2,605 Mpox / orthopox confirmed cases (number also includes Long Beach and Pasadena).
LA County Public Health information on the Mpox vaccine can be found at: http://publichealth.lacounty.gov/media/monkeypox/pride.htm.
******************************************************************************************

Paulo Murillo is Editor in Chief and Publisher of WEHO TIMES. He brings over 20 years of experience as a columnist, reporter, and photo journalist. Murillo began his professional writing career as the author of “Love Ya, Mean It,” an irreverent and sometimes controversial West Hollywood lifestyle column for FAB! newspaper. His work has appea
******************************************************************************************
The preceding article was previously published by WeHo Times and is republished with permission.
Monkeypox
Mpox prevention, vaccinations for this year’s LGBTQ events urged
The CDC on Monday issued a Health Alert Network Health Update on the potential risk for new mpox cases urging vaccinations
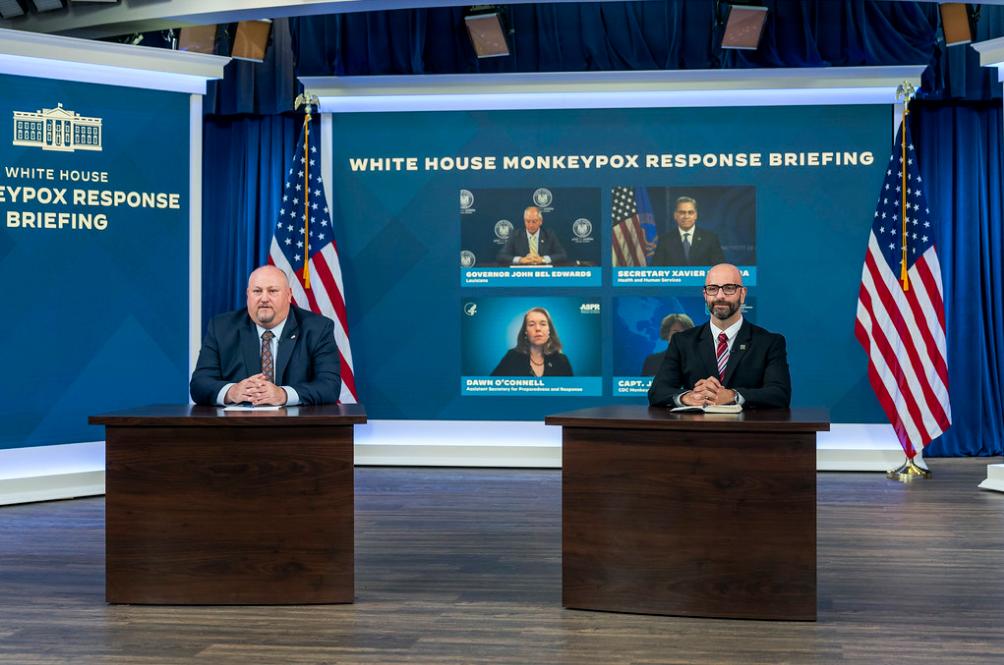

ATLANTA – Federal health agencies, in coordination with their state and local counterparts and community partners, are exploring opportunities to offer mpox prevention initiatives and vaccinations at LGBTQ events this summer, Dr. Demetre Daskalakis said on Thursday.
Daskalakis, deputy coordinator for the White House national mpox response, described these deliberations in response to a question from the Washington Blade during a media telebriefing update on mpox that was hosted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The CDC on Monday issued a Health Alert Network Health Update on the potential risk for new mpox cases.
Since the peak of about 460 cases per day in August 2022, new cases have steadily declined, but following the cluster recently reported in the Chicago area, the update warns, “spring and summer season in 2023 could lead to a resurgence of mpox as people gather for festivals and other events.”
“We have the vaccine, and we have organizations that are willing to do it,” Daskalakis said during Thursday’s call, adding that resources are available and can be deployed flexibly because they are built into existing “HIV and STI funding to allow for this work.”
And the Mpox Crisis Response Cooperative Agreement, Daskalakis said, “provides even more resources locally for such efforts.”
Daskalakis and CDC Mpox Response Incident Manager Dr. Christopher R. Braden also briefed reporters on findings from new studies on the efficacy of the JYNNEOS vaccine for the prevention of mpox.
That data, per the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, reveals that “Among gay, bisexual, and other MSM and transgender adults aged 18–49 years, 2 doses of the JYNNEOS vaccine were 86% effective against mpox, indicating substantial protection against mpox.”
Additionally, “All routes of vaccine administration provided similar protection.”
Monkeypox
Center for Black Equity awarded grant to combat monkeypox
The grant funds the continuing fight against monkeypox misinformation and lack of access to vaccines & resources within minority communities
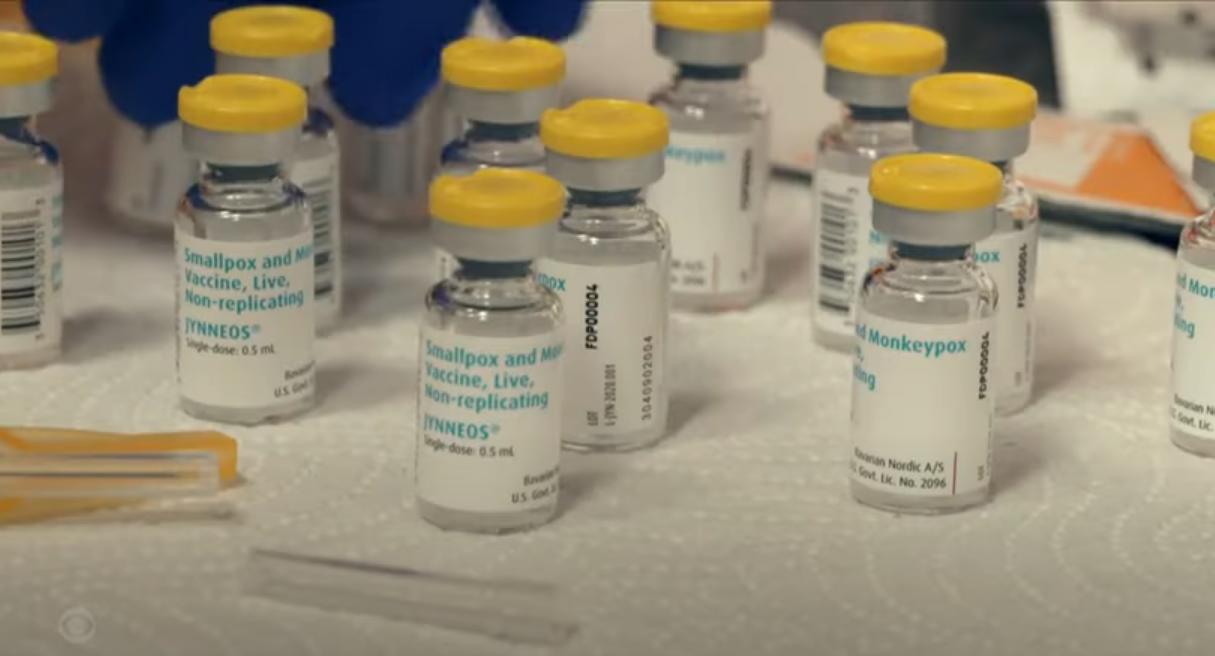
WASHINGTON – The Center for Black Equity (CBE) has received a $50,000 grant supporting the center’s mission to raise awareness about monkeypox in Black and Latinx LGBTQ communities. The grant will also fund the center’s continuing fight against monkeypox misinformation and lack of access to vaccines and resources within these communities.
The grant, which is a part of a partnership with Gilead Pharmaceuticals, requires the CBE to demonstrate that it has the history and capacity to create and implement a community-wide initiative focusing on monkeypox education and boosting vaccination rates in the Black and Latinx LGBTQ communities.
The CBE is a coalition of international LGBTQ community members, Pride organizations, and community-based organizations that have conducted philanthropic and advocacy work in the LGBTQ community for more than 20 years.
Grant funds will be used in efforts to connect Black and Latinx LGBTQ persons with local community-based organizations that will provide accurate and up-to-date information on monkeypox, direct people to vaccination sites, and improve these communities’ access to monkeypox education and vaccines.
The official kickoff of the CBE’s monkeypox initiative started with a nationwide community leader talk.
“We brought together all of the Black Pride leaders from around the country to talk about monkeypox in their communities, what kind of resources they have, what has been the health department response and what do they need to do their work better,” CBE deputy director Kenya Hutton said.
The CBE will continue to host regular talks with community leaders to support the center’s goal of connecting the needs and voices of the Black and Latinx LGBTQ communities on a nationwide level.
“It’s going to get an idea of what it sounds like or what experiences are from community leaders on the ground level,” Hutton said.
Since monkeypox was officially labeled a public health emergency in the U.S., the LGBTQ community has been vocal about the misinformation surrounding the disease as well as limited resources for LGBTQ communities of color. Many have compared the public health response to monkeypox to the early response to the HIV/AIDS epidemic in the 1980s.
“In the beginning, the information seemed to focus on white gay men,” Hutton said. “And even though they keep saying the number of monkeypox cases are decreasing, the numbers are increasing in the Black and Latinx communities.”
The CBE has an interactive map on its website where you can input your zip code and find permanent and pop-up vaccination sites near you. You can also sign up for the CBE’s biweekly newsletter with up-to-date monkeypox information online.
Monkeypox
GLAAD examines impact of HIV, COVID, & MPV in new report
A new GLAAD report is out. Invisible People: A Retrospective Report On The Impacts of COVID & HIV In The United States


By Darian Aaron | NEW YORK – On October 6, in a TIME Magazine exclusive, GLAAD released “Invisible People,” a first-of-its-kind report detailing the disruption caused by COVID-19 in the lives of people living with HIV. The 23-page report combines a comprehensive analysis of peer-reviewed scientific literature, qualitative interviews of people living with HIV, affected communities, and community-based organizations (CBOs) serving these populations.
With research conducted by global market research company Ipsos and completed before the U.S. emergence of the monkeypox virus (MPV), GLAAD has included an MPV addendum to the report that elevates the disproportionate impact of MPV, HIV, and COVID-19 among Black Americans. Through data and first-person narratives, the report highlights the source of medical mistrust in Black communities, examines the lack of access to consistent healthcare during the pandemic, and most recently, inadequate access to the JYNNEOS MPV vaccine, despite the disproportionate occurrence of MPV among Black gay and bisexual men.
GLAAD President Sarah Kate Ellis draws a parallel between the devastating outcomes for LGBTQ people of color across the three major health crises.
“LGBTQ people and queer people of color are disproportionately affected in the pandemic, yet data collection didn’t begin for months to help guide responses and resources, and our voices were vastly underreported across the media,” Ellis says. “These are painful parallels to the early days of HIV/AIDS when GLAAD was formed to fight inaccuracy and invisibility.”
As of October 12, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has confirmed 27,022 MPV cases across the United States. A steady decline in new cases—a national seven-day moving average of 63 cases as of October 12—is attributed to vaccinations and behavioral changes among gay and bisexual men. However, data from the CDC confirms that while Black and Latino gay and bisexual men represent the overwhelming majority of MPV cases, white and Latino men have received their first dose of the vaccine at a much higher rate.
The inequity in vaccine distribution and the reality that unvaccinated people are 14 times more likely to acquire MPV has exacerbated racial healthcare disparities in Black communities that existed long before the current outbreak.
Is history repeating itself?
In a separate interview, pioneering HIV activist Phill Wilson, founder of The Black AIDS Institute, says the “parallels are scary” in the context of the U.S. response to the early HIV/AIDS crisis and the slow response to the threat of MPV among Black gay and bisexual men in 2022.
“During the early days of the HIV/AIDS pandemic, I used to quote my grandmother—probably your grandmother, too: “When white people get a cold, Black people get pneumonia,” Wilson says.
“The parallels are scary—first, the denial, then the blaming, then the slow response and missed opportunities. And finally, the disproportionate impact on Black, other POC (people of color), and poor communities,” he adds.
“All the earliest information about how the COVID-19 pathogen was transmitted said that Black, brown, and poor people would be disproportionately impacted. And yet, those in power did not develop strategies targeting those communities. The opposite happened.”
A California resident, Wilson provides a first-person account of his vaccination experience in Van Nuys, a suburb of Los Angeles situated in the San Fernando Valley.
“I showed up at the pop-up vaccination station at about 10:15 in the morning. They didn’t open until 11:00 am. There were already 100 people in line,” Wilson says. “They had 400 vaccines available that day. By the time I left at 3:00 pm, they had closed the line for the day. I counted less than five Black men, four or five Latino men, and maybe one Asian man getting vaccinated. Four hundred, presumably LGBTQ+ people, were vaccinated that day, and less than 3% were BIPOC (Black Indigenous People of Color).”
To combat the inequity in the MPV vaccine rollout, the CDC has created a Vaccine Equity Pilot Program to reach populations most affected by MPV but less likely to be vaccinated.
In the report, GLAAD also calls out the inherent homophobia that precipitated the naming of HIV as a “gay disease” in the early days of the epidemic. This stigmatizing language has also been echoed during the recent MPV outbreak because most cases are among gay and bisexual men.
Ryan Lee, an Atlanta-based writer, was diagnosed with MPV in July and has since recovered. He says he understands why gay men are reluctant to bare the social responsibility of MPV.
“The burden and shame that gay men have borne regarding our sexual health have created generational trauma and anxieties. And five months of monkeypox have already stoked the bigotry and judgment in those who love telling gay folks how sick and dirty we are,” Lee says.
“So I understand the reluctance of queer folks to be closely associated with a new illness, but we must recognize monkeypox is currently a disease that disproportionately impacts gay men.”
According to reports published in August, the fear and anxiety experienced by many gay and bisexual men and the refusal of some phlebotomists to administer the MPV vaccine are reminiscent of a dark era in our nation’s history that many hoped never to repeat.
“There is something spooky about sitting in a folding chair in 2022, surrounded by other gay men in folding chairs, waiting to be vaccinated by healthcare workers who wear personal protective equipment and immediately wipe down each vacated chair with disinfectant,” says Amanda Cary, manager for the gay men’s sexual health clinic at Whitman-Walker in D.C, in a story published in The Washington Post.
“Invisible People” lays bare the outcome of slow to no inaction when three health crises converge and target an already marginalized group of people. Through this report, GLAAD continues to elevate the stories and voices of LGBTQ people living with HIV at greater risk for COVID and MPV acquisitions.
“We have to learn from the lessons of each epidemic to be better prepared for the next,” says Andres Cantero Jr., a study participant. “People living with HIV, like all chronic conditions, should know that we can count on care that keeps us alive and helps prevent the spread of HIV.”
“We just lost two years,” says Ellis. “We need folks to look up, wake up, and realize that we as a community and a country can walk and chew gum at the same time. We can deal with a major pandemic while not forgetting about our most marginalized folks.”
Read the complete GLAAD report Invisible People: A Retrospective Report On The Impacts of COVID & HIV In The United States.
*******************

Darian Aaron is the MPV project coordinator for GLAAD. He is also communications director of CNP (Counter Narrative Project), and editor-at-large of CNP’s digital publication The Reckoning.
His work can also be read across multiple platforms as a contributor for Q Digital. Follow him on Twitter @darianoutloud.
Monkeypox
LA County Public Health expands Monkeypox vaccination eligibility
Eligible residents can go to a Public vaccinating site or visit Myturn.ca.gov to find other vaccinating sites near you
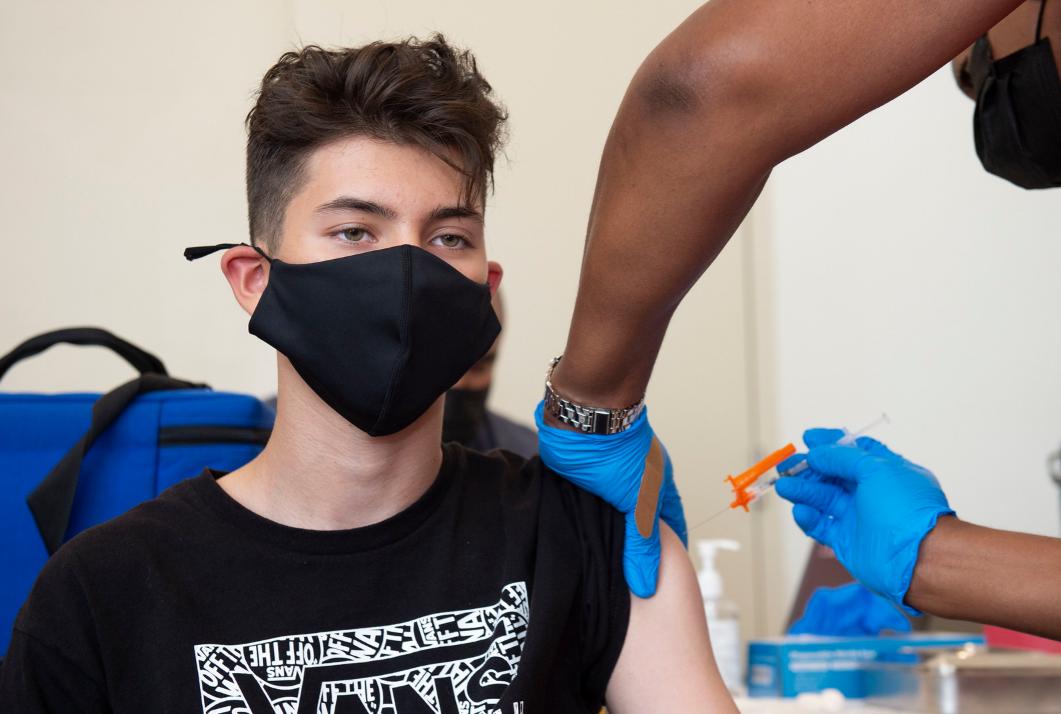
LOS ANGELES – The Los Angeles County Department of Public Health has expanded eligibility to the monkeypox vaccine to closely align with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recent expansion, which includes persons in select occupational groups whose jobs may expose them to orthopoxviruses (such as monkeypox).
Monkeypox vaccine will be available to residents who self-attest to being in the following groups:
- Gay, bisexual or other men who have sex with men or transgender people who have sex with men or other transgender people
- Persons of any gender or sexual orientation who engage in commercial and/or transactional sex
- Persons living with HIV, especially persons with uncontrolled or advanced HIV disease
- Persons who had skin-to-skin or intimate contact with someone with suspected or confirmed monkeypox, including those who have not yet been confirmed by Public Health
- (NEW) Sexual partners of people in any of the above groups
- (NEW) People who anticipate being in any of the above groups
Monkeypox vaccine is also available for persons in select occupational groups whose may be exposed to orthopoxviruses including:
- Research laboratory personnel working with orthopoxviruses
- Clinical laboratory personnel performing diagnostic testing for orthopoxviruses
- Designated public health response team members
- Health care personnel who administer ACAM2000 (Smallpox [Vaccinia] Vaccine)
- Designated health care workers who care for persons with suspected or confirmed orthopoxvirus infections, including clinicians and environmental services personnel
Note that the risk of monkeypox transmission remains very low for health care workers if appropriate personal protective equipment is worn and other infection control practices are followed.
Eligible residents can go to a Public vaccinating site or visit Myturn.ca.gov to find other vaccinating sites near you.
Residents do not need to show ID in order to get a vaccine at sites run by Public Health. However, because residents may need to show vaccination record and ID if you travel or visit certain venues, it is recommended that when getting a vaccine that residents provide the name that is on their ID.
Residents who met prior eligibility criteria can still get vaccinated (see below for prior criteria).
Gay or bisexual men or transgender people who:
- Had multiple or anonymous sex partners in the past 14 days
- Had skin-to-skin or intimate contact with persons at venues or events in the past 14 days
- Had a history of early syphilis or gonorrhea in the past 12 months
- Are on HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP)
- Had anonymous sex or sex with multiple partners in the past 21 days in a commercial sex venue or other venue.
Residents who have monkeypox symptoms or are currently under isolation for monkeypox, should not come to the vaccination clinics or walk-up sites. If residents think they have monkeypox, they should speak with a provider and get tested. If residents do not have a provider, residents can call the Public Health Call Center for more information on monkeypox, including general information, testing, treatment, and vaccines at (833) 540-0473 (open 7 days a week 8am – 8:30pm).
For more information, please visit: http://publichealth.lacounty.gov/monkeypox/.
Monkeypox
Los Angeles County Supervisors approve sick leave for monkeypox
Both coronavirus and the monkeypox outbreak has disproportionately affected essential workers, who are predominantly Black and Latino
LOS ANGELES – The Los Angeles County Board of Supervisors unanimously passed a motion Tuesday, sponsored by Supervisors Hilda Solis and Sheila Kuehl, which directs County attorneys to report back to the board in three weeks on how the County could implement a paid sick leave policy for people who contract monkeypox, or other new and emerging infectious diseases.
The Board also is urging California Governor Gavin Newsom to extend the state’s coronavirus supplemental paid sick leave by signing the AB-152 COVID-19 relief leave bill.
Supervisor Solis prior to the vote pointed out that both coronavirus pandemic and the monkeypox outbreak has disproportionately affected essential workers, who are predominantly Black and Latino.
Solis further noted that without a form of paid sick leave, are in most cases, unable to take the recommended five to 10 days to isolate for COVID-19 — much less the two to four weeks needed to isolate for the duration of a monkeypox diagnosis as recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as well as the County Dept. of Public Health .
During a monkeypox townhall hosted by the Blade in East Los Angeles last week, which was also attended by Supervisor Solis, Sherrill Brown, M.D, AltaMed’s Medical Director of Infection Prevention, in her presentation noted the need for economic relief.
In her practice treating primarily Latino monkeypox cases at AltaMed clinics in Los Angeles and Orange Counties, she told the townhall attendees she was hearing some of her patients were having difficulty with the required isolation protocols because of their economic needs.
Monkeypox
Unvaccinated 14 times more likely to contract monkeypox
Racial disparities persist in new cases of monkeypox as Black & Latino people are overrepresented in the numbers

WASHINGTON – U.S. health officials are celebrating preliminary data on the vaccine used in the monkeypox outbreak, which has led them to conclude eligible persons who didn’t get a shot were 14 times more likely to become infected than those who are vaccinated.
The new data, as described by health officials on the White House monkeypox task force during a call with reporters on Wednesday, comes as the overall number of new cases of monkeypox is in sharp decline, although considerable racial disparities persist in the remaining cases as Black and Latino people are overrepresented in the numbers.
Rochelle Walensky, director of the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, said during the conference call the preliminary data — collected from 32 states between July 2022 and September 2022 — provides an early shapshot of the effectiveness of the vaccine and cause for optimism on the path forward.
“These new data provide us with a level of cautious optimism that the vaccine is working as intended,” Walkensky said. “These early findings and similar results from studies and other countries suggest even one dose of the monkeypox vaccine offers at least some initial protection against infection.”
Walensky during the conference call admitted the data is incomplete in numerous ways. For example, the data is based on information on individuals who have obtained only the first shot as opposed to both shots in the two-shot vaccination process. (The data showing positive results from individuals who have only one shot contradicts previous warnings from the same U.S. health officials that one shot of the monkeypox vaccine was insufficient.)
The data also makes no distinction between individuals who have obtained a shot through subcutaneous injection, a more traditional approach to vaccine administration, as opposed to intradermal injection, which is a newer approach adopted in the U.S. guidance amid the early vaccine shortage. Skeptics of the new approach have said data is limited to support the idea the intradermal injection is effective, particularly among immunocompromised people with HIV who have been at higher risk of contracting monkeypox.
Not enumerated as part of the data were underlying numbers leading health officials to conclude the unvaccinated were 14 times more likely to contract monkeypox as opposed to those with a shot, as well as any limiting principle on the definition of eligible persons. Also unclear from the data is whether individual practices in sexual behavior had any role in the results.
Despite the positive data on the monkeypox vaccine based on one shot, U.S. health officials warned during the conference call the two-shot approach to vaccine administration is consistent with their guidance and more effective.
Demetre Daskalakis, the Biden administration’s face of LGBTQ outreach for monkeypox and deputy coordinator for the White House monkeypox task force, made the case that for individuals at risk obtaining a second dose is “really important.”
“So we see some response after the first [shot] in the laboratory, but the really high responses that we want to really get — that you know, level 10 forcefield as opposed to the level five forcefield — doesn’t happen until the second dose,” Daskalakis said. “So the important message is this just tells us to keep on trucking forward because we need that second dose at arms that people haven’t gotten the first should start their series of two vaccines.”
Also during the call, health officials said they would be expanding opportunities for vaccines as pre exposure prophylaxis, as opposed to practices in certain regions granting vaccines in their limited supply to individuals who meet certain criteria or have had risk of exposure.
The Centers of Disease Control & Prevention, officials said, is also updating its guidance to allow injection of the vaccines in places other than a patient’s arm.
Daskalakis said fear of stigma about getting a noticeable shot in the forearm after obtaining a monkeypox vaccine was a key part of the decision to issue the new guidance on implementation.
“Many jurisdictions and advocates have told us that some people declined vaccine to monkeypox because of the stigma associated with the visible but temporary mark often left on their forearm,” Daskalakis said. “New guidance from CDC allows people who don’t want to risk a visible mark on their forearm to offer a vaccine on their skin by their shoulder or their upper back. Those are areas more frequently covered by clothes.”
Monkeypox
Supervisor Hahn to host Downey & Long Beach vax pop-ups
“This vaccine is critical to keeping people safe from the MPOX virus and I want to make it as easy as possible for people to get vaccinated”
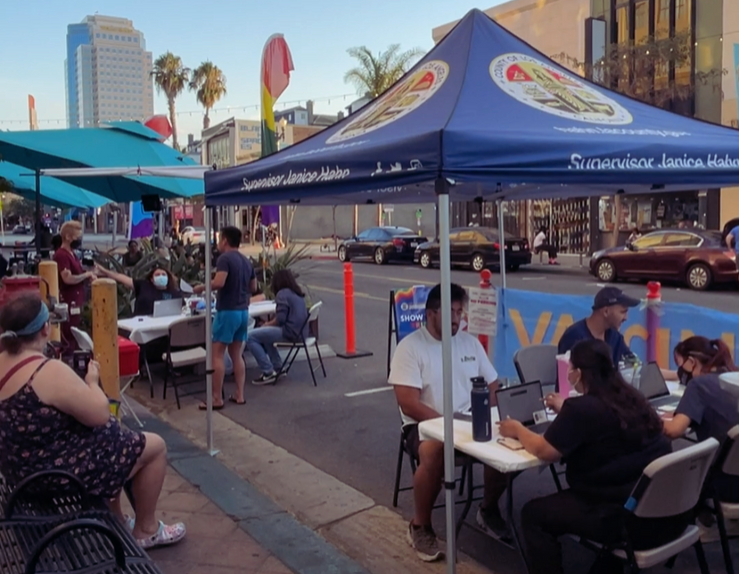

DOWNEY, Ca – Los Angeles County Supervisor Janice Hahn will host a series of Mpox vaccine pop-up clinics outside of bars in Downey and Long Beach this coming weekend. These follow a successful Mpox vaccine pop-up that the Supervisor held outside of Hamburger Mary’s in Long Beach earlier this month, where 67 people received a dose.
“This vaccine is critical to keeping people safe from the MPOX virus and I want to make it as easy as possible for people to get vaccinated,” said Supervisor Hahn. “I am partnering with the LA County Department of Public Health, Long Beach Public Health, and the City of Downey to bring these pop-up vaccine clinics to places where people spend their free time and that are considered safe spaces by the LGBTQ+ community.”
Muevelo Fridays is an LGBTQ+ Latino dance party held once a week at The Epic Lounge in Downtown Downey. Falcon and Falcon North are well-established bars serving Long Beach’s LGBTQ+ community. The Falcon is located on East Broadway, home to several other gay bars that attract people from across the region.
“We appreciate that the Supervisor listens to community concerns, especially when it comes to public health, and we’re grateful that she’s using her resources at the county level to bring the mobile testing unit to Downey,” said Downey Councilman Mario Trujillo, who worked with Supervisor Hahn’s office to bring the pop-up to Downey on Friday. “We invite Downey residents and residents from surrounding communities to take advantage of the unit that’s being brought locally for their benefit.”
The vaccine pop-ups are carried out using a cargo van mobile unit. Supervisor Hahn purchased one of these mobile vans to bring COVID-19 vaccines to communities across her district.
On-site vaccination staff are employees of the Los Angeles County and Long Beach public health agencies.
What: Supervisor Janice Hahn Mpox vaccine pop-ups
Details:
| Friday, September 23, 8pm to 10:30pm Muevelo Fridays The Epic Lounge 8239 2nd St., Downey, CA 90241 |
| Saturday, September 24, 8pm to 12am Falcon 1435 East Broadway, Long Beach, California 90802 |
| Sunday, September 25, 5pm to 9pm Falcon North 2020 East Artesia Boulevard, Long Beach, California 90805 |
Monkeypox
Racial disparities persist in monkeypox outbreak
With the racial disparity ongoing, health observers say additional efforts are needed to reach out to marginalized communities
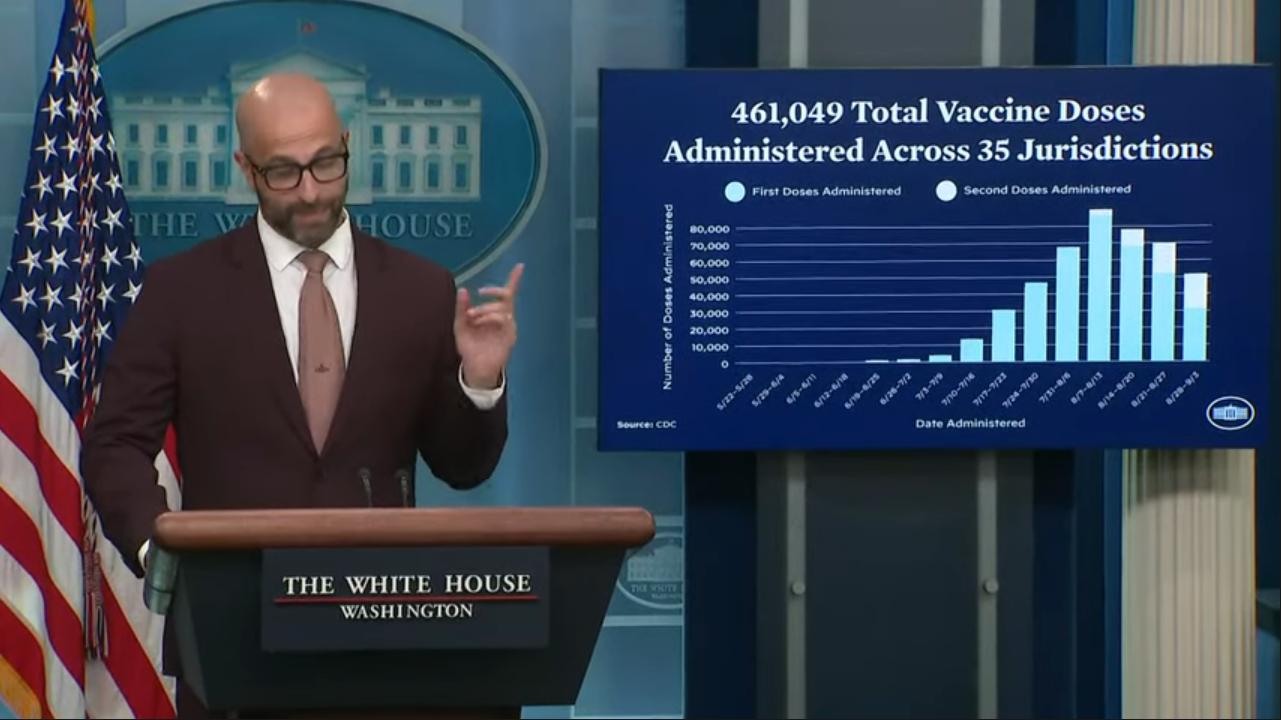
WASHINGTON – Racial disparities persist in response to the monkeypox outbreak as the numbers of Black and Latino men contracting the disease are now disproportionately high, but that inequity is getting new attention as overall cases drop.
Although overall new cases in the monkeypox outbreak are steadily on the decline after numbers peaked in the summer, a growing share of the continuing numbers belong to men who have sex with men who are racial minorities.
The latest numbers show the racial disparity dramatically. In the week of Sept. 4, Black people consisted of 41 percent of the cases and Latinos consisted of 27 percent, while 26 percent were white and three percent were Asian, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control.
Black people among the new cases of monkeypox were much smaller when numbers were first reported earlier in the summer. For example, the percentage was 18 on June 22 and as low as 8 percent June 8. The percentage of Latinos, as with white people, has been on the decline, although they’re still overrepresented in new cases in the context of their demographics in the U.S. population at large.
The disproportionate impact of new monkeypox cases on racial minorities hasn’t gone unnoticed. As a result, health officials are attempting to shift the focus of the monkeypox outbreak away from gay and bisexual men and other men who have sex with men more broadly and more toward men of color who are sexual minorities.
Sean Cahill, director of health policy research at the Boston-based Fenway Institute, said in an interview with the Washington Blade the racial disparities in the monkeypox outbreak are largely the result of Black and Latino men being “less likely to get vaccinated than their proportion of the population.”
“So they’re more vulnerable to monkeypox, and they’re less likely to get the vaccine,” Cahill said. “So that’s a real problem, and it’s really critical that you know, federal, state and local partners come together and really center equity in the response and try to reduce the burden on Black and Latino gay men, but also increase access to the vaccine to ensure that people can protect themselves.”
The Fenway Institute last week issued a blueprint calling for a more effective federal response to monkeypox, accusing the U.S. government of failing to effectively mobilize existing public health infrastructure to aid communities affected by the virus. The document outlines a range of possible actions, but also concludes marginalized communities are having difficulty accessing vaccines and treatments, which are concentrated at well-resourced institutions less accessible to communities of color.
Cahill, asked to characterize whether the numbers demonstrating racial disparity have changed over time or have remained stagnant, said any trends are difficult to determine because the data on racial demographics has been available only recently and “it’s very imperfect data.”
“I don’t know if it’s getting worse or better, the disproportionate racial ethnic impact,” Cahill said. “But it’s definitely there, and it doesn’t seem to be going away.”
The Biden administration, while touting the 20 percent decline in overall cases in the monkeypox outbreak, has also started to recognize the continued disproportionate impact of monkeypox on Black and Latino men who have sex with men.
Rochelle Walensky, director for the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, said during a conference call with reporters the U.S. government approaches the decline with “cautious optimism.”
“Over the past several weeks, we have also seen the racial and ethnic makeup of this outbreak evolve,” Walensky said. “While monkeypox cases were first seen predominantly in non-Hispanic white men, in the last week, among the cases for which we have race and ethnicity data, non-Hispanic Black men represented 38 percent of cases, Latino or Hispanic men represented 25 percent of cases, and non-Hispanic white men represented 26 percent of cases.”
Among the efforts the Biden administration has undertaken is a pilot program for vaccines reserved for large events and equity. Monkeypox vaccines have been administered to more than 10,000 people, including at Southern Decadence in New Orleans, Atlanta Black Gay Pride, Charlotte Pride, Boise Pride Festival, and Oakland Pride and Pridefest.
Dr. Demetre Daskalakis, the face of LGBTQ outreach for the Biden administration in monkeypox efforts and deputy director the White House monkeypox task force, was among those promoting the pilot program in equity efforts during a conference call with reporters.
“Health departments will use their local experience and connection to the community to identify hyperlocal strategies to improve vaccine access to communities of color, specifically those that are overrepresented in this outbreak,” Daskalakis said.
David Johns, executive director of the National Black Justice Coalition, said in the racial disparities in the monkeypox outbreak are consistent with other trends in public health.
“There have been so many opportunities to learn ways to address health inequities before they grow,” Johns said. “That Black people continue to be disproportionately impacted by this newest health epidemic is additional evidence of how white supremacy works and the importance of democratized responses to crises.”
Biden health officials, asked by the Washington Blade during the virtual meeting why the administration’s stated goal of equity in managing the monkeypox outbreak isn’t producing racial equity among new cases, restated their efforts and talked about the difficulty in achieving that goal.
Walensky, who has also had a lead role in the Biden administration combating the coronavirus pandemic, said racial disparities in the monkeypox outbreak “is not uncommon for many infectious diseases, quite unfortunately,” and defended the U.S. government’s approach to monkeypox.
“And it is exactly for these reasons why we started on these pilot projects before we even saw the shifts in data, as that is often the case in infectious diseases that we have more vulnerable population — racial and ethnic minorities — who are most impacted later on,” Walensky added. “And so, we anticipated this. We have embarked on these activities to address this in exactly this moment.”
Daskalakis, following up in defense of the Biden administration’s efforts on equity, said he’s “spoken to providers on the ground and also promoters at these events who have noted that this effort is really unprecedented in terms of reaching deeply into these communities.”
“I think all of our commitment in the administration is to really focus efforts on equity to resolve the issues that we’re seeing. It is a hard effort and it’s a challenge,” Daskalakis added. “And I think that the way to address equity is intentionally, and this is an example of intentional work to address equity.”
With the racial disparity in the monkeypox outbreak ongoing, health observers say additional efforts are needed to reach out to marginalized communities to ensure they have access to public messaging and vaccinations.
Cahill said although people of color in urban areas go to LGBTQ centers to receive health care, many of them are also getting care through other facilities that aren’t LGBTQ-specific, such as emergency rooms and urgent care clinics .
“I think providing some training and technical assistance to those healthcare organizations in how to provide affirming care to bisexual men could be an important approach and could make it so that people might be more likely to disclose same-sex behavior in those contexts,” Cahill said.
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoLegendary organizing activist Dolores Huerta, 95, rides in AHF’s ‘Food for Health’ Rose Parade float
-

 Commentary4 days ago
Commentary4 days agoNew Year, New Queer: A polite reminder of the traditions that many of us make and many of us break that are well worth revisiting this particular year
-

 Tarot Readings and Astrology3 days ago
Tarot Readings and Astrology3 days agoJanuary is calling for us to be grown-ups in Intuitive Shana’s New Year tarot reading
-

 Books2 days ago
Books2 days agoA look back at the best books of 2025
-

 LGBTQ+ Youth Mental Health2 days ago
LGBTQ+ Youth Mental Health2 days agoLaw expanding mental health resources for LGBTQ+ youth has gone under effect
-

 Parks & Recreation5 days ago
Parks & Recreation5 days agoFor more than two decades, Los Angeles Neighborhood Land Trust has worked to address park inequities
-

 Television1 day ago
Television1 day agoThe ‘Stranger Things’ coming out scene: The reaction and the relevance





